
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways:
-
Kadena is an enterprise-grade, Layer 1 Proof-of-Work blockchain.
-
Pact is Kadena’s native smart contract language with an inbuilt bug-detecting feature.
-
The Kadena ecosystem includes a gas station, NFTs, DEXs, Wallets, and other DeFi apps.
-
KDA is Kadena’s native currency for incentivizing miners and paying transaction costs.
Blockchain technology can revolutionize the world as we know it with its potential to build trustless applications. From smart contracts to tokenized real-world assets, developers are just beginning to scratch the surface of the potential of this revolutionary technology. However, if you have ever tried to create a blockchain application, like a decentralized exchange (DEX), you may have encountered many hindrances that may have shut down your dream.
Businesses and individuals who want to adopt blockchain in their systems often encounter issues like lack of interoperability (the ability of blockchains to communicate and share data seamlessly) and scalability (the ability of blockchains to process and store a large number of transactions.) Additionally, they expose themselves to faulty smart contracts, which are complex and expensive to build and deploy.
Kadena is an enterprise-grade hybrid blockchain striving to change the narrative by offering developers and users a new smart contract programming language and a set of cutting-edge development tools. In doing so, the platform hopes to provide a blockchain solution that is interoperable, scalable, and energy-efficient. Follow along as we discuss what Kadena is, how it works, its main features, the Kadena ecosystem, and the Kadena token (KDA).
What is Kadena?
Kadena is an enterprise-grade, Layer 1 Proof-of-Work (PoW) blockchain. It aims to offer a highly scalable and developer-friendly hybrid blockchain that guarantees a level of security similar to Bitcoin. To achieve this, Kadena leverages a novel consensus mechanism known as Chainweb and the Pact programming language.
Kadena’s mission is to perfect its base layer for scalability and developer purposes without needing Layer 2 scalability and functionality protocols. These protocols can complicate app development; therefore, offering a complete tool kit on one platform will undoubtedly be more developer-friendly. The Kadena team claims Kadena can handle up to 480,000 transactions per second across 20 chains, and as it upgrades to 50 chains working in parallel, they expect it to exceed 1million transactions per second.
The network’s native programming language, Pact, is engineered to improve upon major drawbacks plaguing Ethereum’s Solidity, especially its vulnerability to unrestrained loops and lack of Formal Verification. Formal Verification is a way of proving that the algorithms underlying a system is functioning properly within its bounds. Moreover, developers can upgrade Pact smart contracts anytime without needing a hard fork.
Kadena has also developed a private blockchain to precede its public smart contract blockchain. The private chain, dubbed Kadena Kuro, features a Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) consensus method and is designed for enterprise-grade applications. Since 2018, a healthcare consortium has been using Kuro to streamline the process of gathering and maintaining insurance data. Essentially, Kuro runs as a side-chain alongside Kadena’s public blockchain to boost transactions and build new data markets.
Who Founded Kadena?
Will Martino and Stuart Popejoy co-founded Kadena in 2016. The two happen to have deep ties to traditional finance:
-
Will was the lead engineer of Juno, JPMorgan’s pioneer blockchain project, and initially served as the technical leader of the Securities and Exchange Commission’s (SEC) Cryptocurrency Steering Committee.
-
Stuart is a former member of the JPMorgan Blockchain Center for Excellence blockchain division.

Will Martino, left, and Stuart Popejoy – Kadena co-founders.
Will and Stuart were steerer members of JPMorgan’s blockchain initiatives, where they gained a proper understanding of traditional finance (TradFi) and decentralized finance (DeFi). The understanding helped them to start Kadena to solve the flaws of centralized finance (CeFi) and DeFi. Besides the two, Dr. Stuart Haber, the co-inventor of blockchain and the most cited reference in Satoshi Nakamoto’s Bitcoin whitepaper, is another notable figure that acts as a Kadena advisor.
How Does Kadena Work?
To understand how Kadena works properly, we must consider its architecture. The Kadena architecture consists of three functionalities:
-
Chainweb – a Layer 1 public network that offers limitless scalability in a PoW environment, leveraging a cutting-edge braiding technique (explained later) across parallel chains.
-
Kuro – a Layer 2 open-source private chain optimized for enterprise-grade use cases. It boasts a transaction speed per second (TPS) of 8,000 across 500 nodes.
-
Pact – Kadena’s native open-source programming language that uses Haskell.
Let’s have a closer look at each of these functionalities.
Chainweb
Chainweb is Kadena’s Layer 1 public blockchain that offers unlimited scalability in a PoW consensus environment. It also refers to the exclusive architecture of the Kadena ecosystem. One of the significant issues of PoW networks is their incapability to scale. Chainweb enables Kadena to overcome this problem by introducing sharding (splitting network data to spread the computation and storage into peer chains) and braiding (combining peer chains to support the transactions on the main chain) techniques.
As such, Chainweb is an interconnected bundle of several parallel chains, known as peer chains, which homogeneously work together for one blockchain. The image below demonstrates the Chainweb graph for Kadena’s 20 peer chains.
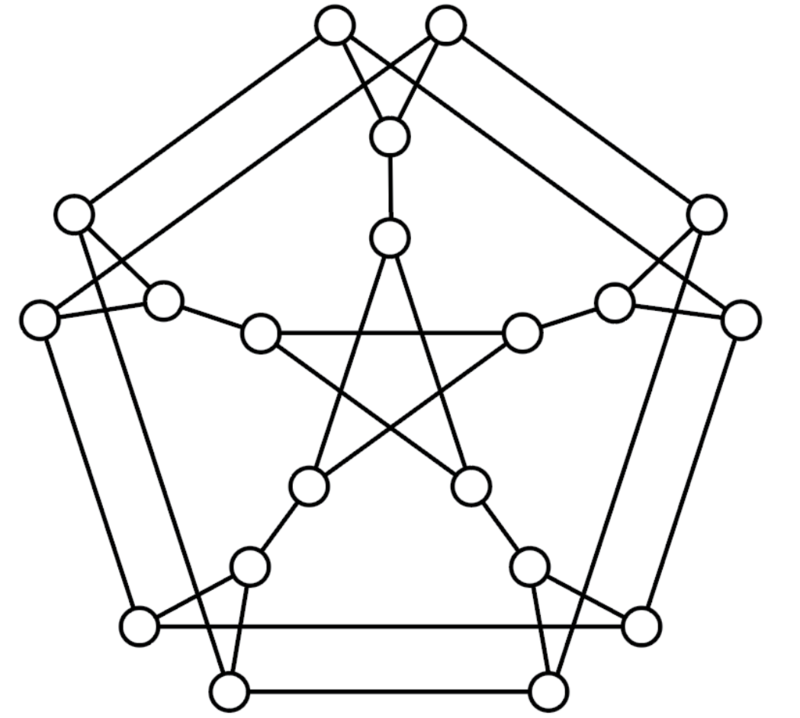
Source: https://medium.com/kadena-io/how-to-scale-a-proof-of-work-blockchain-9233e5b4b62
At first, Kadena launched with ten peer chains. Currently, Chainweb has 20 peer chains with a TPS of 480,000 when integrated with the Kuro chain. Despite doubling its peer chains, tests show that Kadena’s energy consumption remained the same. The results act as proof-of-concept for the network’s plans to scale from 20 peer chains to 1000 and more while consuming the same amount of energy, making it energy-efficient.
Kuro
Kuro, previously ScalableBFT, is Kadena’s private blockchain, which works homogeneously with Chainweb. It’s an open-source Layer 2 chain that leverages a Byzantine Fault Tolerant mechanism and is designed for enterprise-grade applications. Kuro is developed using the Pact programming language. Some of its unique features include:
-
Automatic bug detection via Formal Verification.
-
Human-readable code accessible to developers and other users.
-
The option to change smart contract terms to accommodate dynamic business needs.
-
Easy integration with traditional databases with a native application programming interface (API).
-
Enhanced security alternatives, such as key rotation and pluggable encryption, enable dial-up security to meet user specifications.
Pact
Pact is Kadena’s native smart contract language with an inbuilt bug-detecting feature. It stands out as the first human-readable programming language, which is Turing-incomplete. It enables anyone (tech-savvy and non-tech-savvy users) to build blockchain apps in an up-front, direct, and secure way.
As mentioned, Pact was invented to solve the major problems plaguing basic programming languages, like Ethereum’s Solidity. Since Solidity is Turing-complete (meaning it can compute anything that other computational methods can compute), it’s vulnerable to numerous attack vectors, including unbounded loops. When you reference a code from Pact contracts, you gain control of what happens with your transactions, even after upgrades.
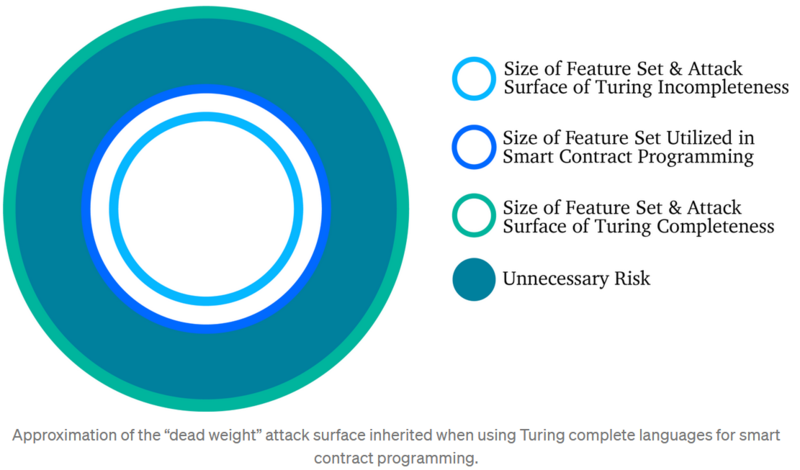 Source: https://medium.com/kadena-io/turing-completeness-and-smart-contract-security-67e4c41704c
Source: https://medium.com/kadena-io/turing-completeness-and-smart-contract-security-67e4c41704c
One of the factors that contribute to a high number of attacks on Turing-complete contracts is recursion. Recursion is the ability of a smart contract to repeat an action until a given condition is met. Contrary, in Turing-incomplete languages like Pact, a recursion creates an instant failure and dismisses any running code. The action substantially minimizes any possible attack vectors in the code. Do you remember the 2016 DAO attack on Ethereum? It stands out as one of the best examples where an attacker exploits the reentrancy feature due to the Turing-complete nature of the code.
Features of the Kadena Network
Kadena strives to act as ‘The Source for the Resources’ necessary to create web3 applications. It overcomes most hurdles hindering blockchain’s mass adoption, including scalability, security, and ease of use.
Scalability
Kadena’s use of the sharding technique boosts the scalability of the network, as every shard only deals with a small portion of the total transactions. This improves Kadena’s transaction throughput since each shard simultaneously handles transactions and creates blocks. The more shards in the network, the more transactions it can handle.
Security
Regarding securing the peer chains, Kadena uses the braiding technique to secure them. All the blocks in the blockchain have hashes of previous blocks and hashes of former blocks in other peer chains. This enables the blocks to validate each other, irrespective of their shards or chains.
For someone to attack the network, they must control more than 51% of the network hash power instead of one or two shards. This mitigates single-shard attacks and secures the Kadena blockchain as a whole. Though braiding is a bit complex, the use of ‘degrees’ and ‘diameters’ in the Chainweb system makes it easier for non-tech and tech-savvy users.
Formal Verification (FV)
FV is a Pact feature that allows developers to automatically confirm whether their contracts contain bugs – loopholes that can be exploited via math computations. You can think of the FV tool as the ‘Grammarly programming tool. Apart from detecting bugs, FV also finds out whether your code executes other activities besides its intended purpose.
Blockchain Governance
Unlike Solidity smart contracts, Pact contracts can be modified or fixed through an update functionality, which lets users introduce new versions of smart contracts. Any abnormality will make the smart contract relapse to its initial state and reject further changes.
The Kadena Ecosystem
Kadena’s ecosystem is rapidly growing with exclusive features, such as a ‘gas station’ and a new non-fungible token (NFT) standard. The ecosystem enables various teams relying on it to build with ease.
Gas Station
This is the first cryptocurrency gas station built on blockchain. Basically, a crypto gas station is an account that compensates all gas used to implement certain smart contract activities to users. The concept behind these stations is to ease the use of decentralized apps (dApps), helping users have a smooth experience without being compelled to acquire native tokens from an exchange and transferring them to a web3 wallet to use them in a dApp.
Wallets
There are multiple wallets integrated with the Kadena blockchain, including:
Chainweaver – The Kadena team is behind this wallet. Chainweaver utilizes 12-word seed phrases to generate all your wallet’s private and public keys.
Zelcore – Zelcore is a third-party wallet that features a combination of usernames and passwords for security. Remember, you are personally accountable for your security. Therefore, an easy-to-crack password puts your assets at risk.
Kaddex
Kaddex is the first Automated Market Maker (AMM) DEX built on Kadena. Because of Kadena’s unique features, Kaddex users can swap crypto with low-cost gas fees while enjoying a Layer 1 PoW network. Kaddex shares a similar vision with Kadena centered on innovative features and law compliance.
NFTs
Kadena’s NFTs, programmed with Pact, solve one major problem hindering Ethereum’s ERC standards – limited utilities (apart from acting as a medium of value transfer). Stuart Popejoy, the Kadena co-founder, claims the NFT royalty sales in various Ethereum markets are left in the hands of markets. This compels users to trust in a space that is meant to be trustless.
Kadena’s native NFT standard would enable automatic royalty transfers to creators even if the sale/transfer were executed outside an NFT marketplace. This ensures and supports the artist’s right to royalties from their works.
What is the Kadena Token (KDA)?
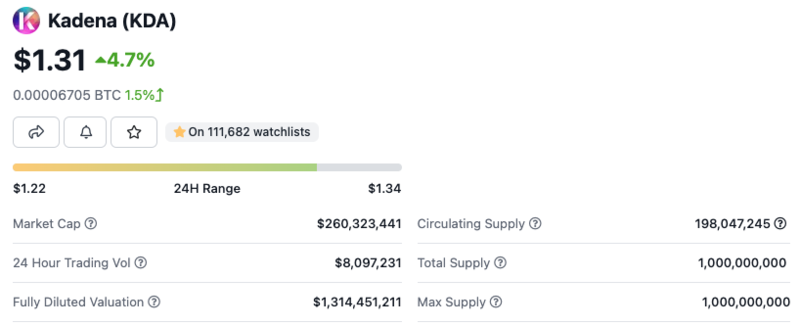
KDA is Kadena’s native currency that facilitates the Kadena ecosystem payments. Like in Ethereum, Kadena users need KDA to pay for transaction charges. On the other hand, miners secure the Kadena blockchain by mining KDA. Essentially, miners confirm transactions and record them in the blockchain as new blocks.
KDA has a maximum supply of 1 billion, with a current circulating supply of 198 million. You can trade it on exchanges such as BKEX, Binance, KuCoin, Gate.io, and OKX. You can check CoinGecko markets to find more marketplaces where you can trade KDA.
Source: https://medium.com/kadena-io/update-to-the-kadena-token-economic-model-21e1ec18f099
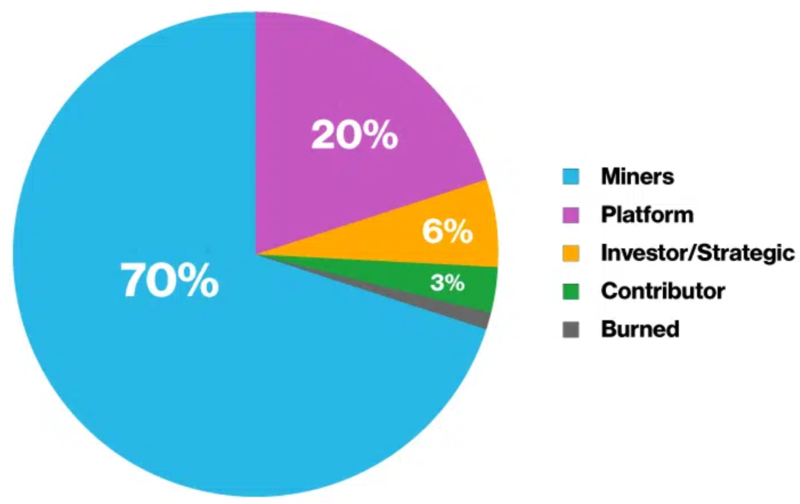
Kadena’s total token allocation is divided into five categories:
Platform reserve: 20% of KDA’s total supply is assigned to the platform reserve. This reserve resembles a treasury where assets will be partially monetized and used to fund services like insurance, code verification, and gas station grants.
Miners: 70% of KDA’s total supply is allocated to miners. The tokens are slowly added into supply as miner block rewards.
Investor/Strategic: 6% of the total supply was sold in funding rounds.
Contributor: 3% of the tokens are assigned to ecosystem contributors, like the staff, consultants, and advisors.
Burned: 1% of the total supply was burned during the initial launch.
Conclusion
Kadena is a promising hybrid blockchain that has already received solid support from businesses, developers, and crypto users. The Kadena team has done impressive work scaling a PoW network without sacrificing security and decentralization features. Currently, Kadena is arguably the fastest chain in the blockchain industry. With its entry into the DeFi and NFT spaces, the scope of its use becomes even more significant.
