Table of Contents
Key Takeaways:
-
A hashgraph is a patented algorithm that provides the benefits of blockchain technology (decentralization, distribution, and security via hashing) without the hitch of low transaction speeds
-
Hedera Hashgraph is governed by the Hedera Governing Council – a fully decentralized entity comprising 39 major world-leading organizations drawn from various industries including Google, LG, and Boeing, where each member enjoys an equal vote over software upgrades, network pricing, treasury decisions, and so on.
Hedera Hashgraph (HBAR) is the native currency for the Hedera network. Blockchain is one of the popular methods of implementing distributed ledger technology (DLT). DLT describes software or infrastructure that allows decentralized ledgers to be shared and verified across multiple locations. Nonetheless, DLTs are not only limited to blockchains! Hedera is a public crypto network and governing entity for creating decentralized applications (dApps) that leverages a unique type of DLT known as hashgraph.
A hashgraph is a patented algorithm that provides the benefits of blockchain technology (decentralization, distribution, and security via hashing) without the hitch of low transaction speeds. While the Bitcoin network boasts around five transactions per second (TPS) and Ethereum 15 TPS, the Hedera network can handle up to 10,000 TPS. Thus, this unique DLT application potentially beats first-generation blockchains in terms of scalability and speed. Join us as we learn more about hashgraph technology and its potential applications in crypto.
What is Hedera Hashgraph (HBAR)?
HBAR is the native currency for the Hedera network. Essentially, Hedera is a DLT network that fundamentally differs from the Bitcoin and Ethereum blockchains but serves the same purposes. It’s based on the security and validation mechanisms considered more efficient than those applied on blockchain networks.
Hedera implements DLT on hashgraph instead of blockchains. Hashgraph technology offers a practical alternative to blockchains for leveraging an open ledger system. The technology presents multiple benefits compared with blockchains. For example, there is no mining, meaning the environmental effect of using it is significantly minimized. It also boasts lower transaction fees of $0.0001 per transaction. Moreover, hashgraph-based networking can implement a DLT with the same security and anonymity perks as blockchain-based ledgers, with added advantages such as improved performance and higher processing capacity.
Currently, the Hedera network is the only DLT implementation based on the hashgraph algorithm, and HBAR is the only hashgraph-based cryptocurrency. Despite being the pioneer project, Hedera offers detailed guidelines and source code illustrations to application programming interface (API) calls, which enable developers to build their crypto projects on the Hedera network.
Hedera is drawing the attention of major technology companies and investors because of its potential to offer the benefits of blockchain-based ledgers while bypassing technical hitches that have kept them from scaling up to handle high transaction volumes. Hedera has already partnered with some of the world’s leading companies, such as Boeing, Google, and IBM, which are members of the Hedera Governing Council.
Hedera Hashgraph (HBAR) Token
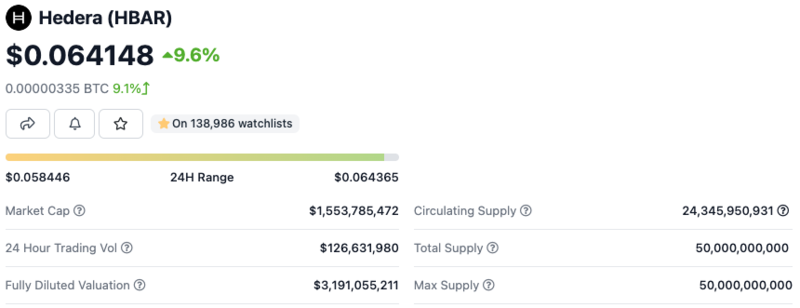
HBAR has a circulating supply of 22.9 billion and a maximum supply of 50 billion. It currently has a market cap of $1.4 billion and ranks 37. Since issuing HBAR tokens doesn’t involve a complex cryptographic consensus, the Hedera network minted all the 50 billion tokens before launching its Mainnet in 2018, allocating these based on the below token distribution:
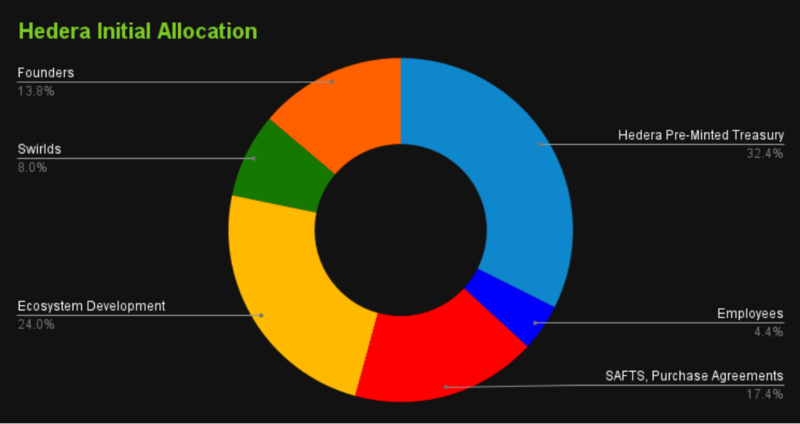
Find out more about Hedera (HBAR)’s tokenomics here.
The HBAR token derives its value from several use cases. First, it acts as Hedera’s utility token. If you participate in validating network transactions as a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) node operator, you will be incentivized to use HBAR tokens. Besides, validators are rewarded with HBAR tokens for securing the Hedera network.
HBAR has also drawn the interest of crypto investors who believe its value will rise as the Hedera network goes mainstream. The network has also positioned itself well to appeal to environmentally-conscious partners and investors by embracing the energy-efficient PoS instead of the energy-intensive Proof-of-Work (PoW) mechanism.
Where to Buy Hedera Hashgraph
You can trade HBAR in over 50 crypto marketplaces, including Binance, HitBTC, KuCoin, Huobi Global, and Bybit.
Remember to do your own research before investing in any cryptocurrency.
How Does the Hedera Hashgraph Work?
Hedera Hashgraph is based on an idea from the graph theory known as directed acyclic graphs. These graphs facilitate the formation of data structures and flows that don’t follow up on former states. When applied as the basis for a DLT network, acyclic graphs ensure transactions can’t be altered once they have been verified and included in the network.
Hedera applies these graphs in its nodes (network validators) to implement an asynchronous byzantine fault-tolerant (ABFT) consensus mechanism. This mechanism is an alternative to slow and resource-intensive cryptographic consensus methods used by blockchain-based ledgers. Hedera strongly believes the ABFT mechanism is more effective, rational, and secure than standard validation methods as transactions are included in the network energy-efficiently and cost-effectively.
Since the network is fully compatible with smart contracts, it can potentially host dApps. This feature enables developers to build apps that support transferring value and goods without third parties, such as banks and brokers. The elimination of intermediaries from the equation makes dApps cost-effective, faster, and more secure than conventional apps. Hedera works through the Hashgraph consensus and governance. Essentially, Hedera’s consensus and governance make it highly scalable and best-suited to become the first hashing DLT network to achieve mass adoption.
Hashgraph Consensus
Hedera Hashgraph is a proof-of-stake (PoS) network leveraging an open-source hashgraph distributed consensus mechanism. Dr. Leemon Baird, the Hedera co-founder and previous Chief Scientist, developed and patented the mechanism. It offers high efficiency in bandwidth application and can process up to 10,000 TPS.
Unlike first-generation proof-of-work (PoW) networks like Bitcoin, which pick one miner to determine the next block, the community of nodes operating the hashgraph mutually agrees on which transactions to include in the ledger. Through gossip-about-gossip and governance voting, the hashgraph network achieves consensus on the legitimacy and timestamp of each transaction. If the transaction is legitimate and falls within the appropriate time, the ledger’s state is updated to record the transaction with 100% finality.
In a blockchain-based ledger, consensus mechanisms require blocks to be verified in one long chain, consented by the node validators. When two blocks are created simultaneously, the validators select one block and reject the other, lest the network split into two chains. It’s similar to a growing tree that continuously has all but one of its branches cut off.
In hashgraph, each package of transactions is added to the ledger – none are cast-off – thus, it’s considered more efficient than blockchain-based ledgers. All the branches are left to exist forever and are knitted together. Besides, a blockchain-based ledger can fail if new transaction requests are made too quickly – in the case of new branches budding faster than they are cut off. This is why blockchains require PoW or some other mechanism to artificially regulate growth. In hashing, transactions are not discarded; hence no need to artificially slow down processes.
Governance
Hedera Hashgraph is governed by the Hedera Governing Council – an entity comprising 39 major world-leading organizations drawn from various industries. These organizations include Google, LG, and Boeing. The council is fully decentralized, and each member enjoys an equal vote over software upgrades, network pricing, treasury decisions, and so on. Besides, the council members are term-limited and are not paid by Hedera.

The council is meant to help Hedera achieve its vision of a completely decentralized, fair, reliable governance in the long-term network interests. Each member is accountable for partial network ownership through the Hedera LLC agreement. You can access minutes from each council meeting within one month after voting.
Hedera’s governance system significantly minimizes the risk of conceptual or personal disagreements affecting most public networks’ governance. To ensure a reliable developer-focused community and developer-driven roadmap, users can send proposals regarding features, functionalities, and standards via the Hedera improvement proposals (HIPs). These proposals are community-based, assessed and accepted by the Hedera Governing Council, and executed by a distributed group of project engineers.
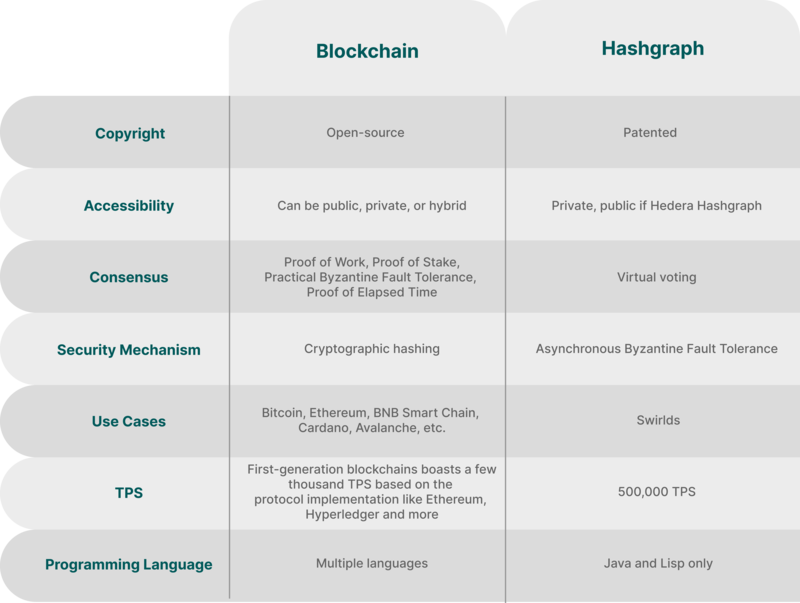
Hashgraph Vs. Blockchain
Blockchain and hashgraph are both DLTs. While they present considerable differences, as shown in the table below, they are applied to securely record and store transaction data. The major difference between blockchain and hashgraph is that the latter involves a consensus algorithm known as gossip-about-gossip, while blockchain mainly leverages PoW or PoS mechanisms.
What is Hedera Hashgraph Used For?
Applications that use Hedera Hashgraph’s network services are an essential element of Hedera’s utility. Anyone – developers, startups, investors, or Fortune 500 companies – can sign up anonymously and run a Hedera-based app on the network across various use cases such as:
-
Payments – Facilitate secure, prompt, and low-cost peer-to-peer (P2P) payments with HBAR, stablecoins, and other tokens.
-
Content authenticity – Control and publicly prove the legitimacy of personal documents, like academic qualifications.
-
CBDC – Issue central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) for national or global remittance purposes.
-
Audit log – Cost-effectively build a publicly auditable data log, such as payable events and internet-of-things (IoT) sensor data.
-
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) – Eliminate expensive third parties and create financial marketplaces, borrowing, and lending protocols with Solidity smart contracts.
-
Decentralized identity – Deploy decentralized identity via secure and anonymous methods.
-
NFTs – Create non-fungible token (NFT) markets for the minting and trading tokens.
-
Permissioned blockchain – Perform private transactions on permissioned blockchains, like Hyperledger Fabric.
-
Interoperability – Create an interoperable bridge linking public and private networks to facilitate value transfer.
Final Thoughts
HBAR is cryptocurrency fueling a unique network, which circumvents most of the drawbacks that have limited the mainstream adoption and usefulness of blockchain-based DLT applications. The patented algorithms behind the Hedera Hashgraph and HBAR are comparatively new and are now scaling up to solve and build on the weaknesses of blockchain technology. However, downsides and inefficiencies in hashgraph technology may emerge as the network grows in terms of users and applications.

