Table of Contents
Key Takeaways:
-
Public and private keys are used to encrypt and decrypt data with the common goal of securing it.
-
Any blockchain user can access a public key, and use it to send messages or funds.
-
A private key is exclusive to the person it was generated for and guarantees access to the sent message or funds.
Public and private keys are strings of characters with (via advanced math) incomparable relationships, through which information encrypted (converted into machine code) with one number can only be decrypted (converted back into human-readable format) with the other number and vice versa. To apply this relationship for security purposes, once two numbers are mathematically generated, one is exclusively accessible (private key) while the other is publicly accessible (public key).
The private key owner can then validate themselves to another person with their public key. Besides, you can use a public key to relay confidential messages to the owner of the conforming private key. This article will take you through cryptocurrency wallets and how they work, what private keys are and their importance, how to store your private keys, what public keys are, and the differences between them.
Cryptocurrency Wallets and How They Work
Cryptocurrency wallets store your private keys – the passwords for accessing your digital assets – safely while maintaining accessibility, enabling you to send and receive digital currencies like Bitcoin and BNB. They come in multiple forms, from hardware wallets like Trezor (which resembles a USB stick) to online wallets like MetaMask, which further simplifies the use of cryptocurrency.
Each has its strengths and weaknesses. For instance, hardware and paper wallets are tougher for hackers to access as they store private keys offline but have few functionalities and are prone to be misplaced or destroyed. On the other hand, online wallets are the easiest way to kickstart your crypto journey and guarantee a balance of security and accessibility. But since they store private keys online, your safety is only as good as your wallet provider’s security.
Essentially, crypto wallets allow you to:
-
Manage your crypto holdings in one place
-
Control your private keys
-
Send and receive crypto to and from other wallets
-
Browse decentralized apps (dApps)
-
Shop at online stores that accept crypto payments
Unlike standard wallets, which store actual cash, cryptocurrency wallets technically do not keep your digital assets. Your assets are held on the blockchain, but you can only access them through a private key. As such, private keys prove ownership of digital assets and allow the rightful owner to execute transactions. The moment you lose your private keys, you lose access to your assets. That is why it’s essential to store your hardware wallet and/or private keys safely. While you can also utilize centralized wallet providers, depositing your crypto on these platforms is essentially handing over ownership of your cryptocurrency to the platform.
What are Private Keys?
You are assigned a unique pair of keys when you download a web3 wallet, like MetaMask or Trust Wallet. You get a public key – a code that enables you to receive digital currencies – and a private key, which allows you to access and control those assets. A private key is an extensive, randomly generated string of alphanumeric characters with multiple digits. Essentially, it acts as a password for accessing a crypto wallet – it grants access to the digital wallet controlling your crypto.
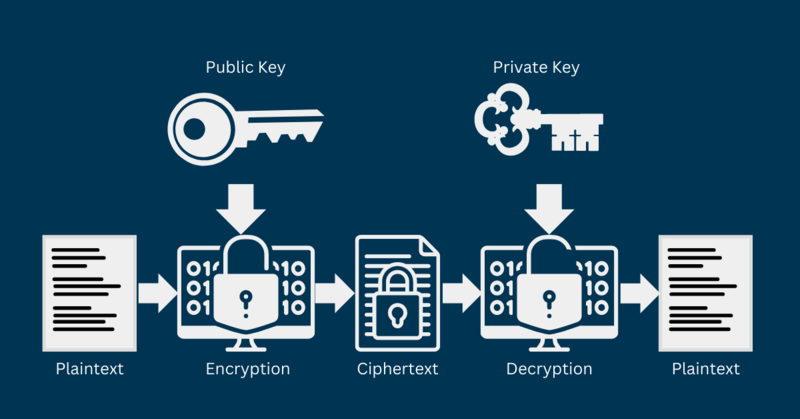
Earlier, we mentioned that cryptocurrency wallets operate with digital keys and addresses, confirming ownership and control over digital assets. A private key is literally a password – you are the only person who owns and knows it (unless it’s compromised) and acts as your digital identity. It gives you access to your wallet and allows you to spend, withdraw, send, and perform any other transaction from your wallet.
Typically, private keys come in all sorts based on your crypto. However, most of them, including Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin, apply 256-bit encryption. For instance, a Bitcoin private key is formatted this way:
0x01 and 0xFFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFE BAAE DCE6 AF48 A03B BFD2 5E8C D036 4140, representing almost the complete range of 2256-1 values.
Why Are Private Keys Important?
Private keys help cryptocurrency users to secure their holdings. Digital currencies, like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and BNB, are decentralized, implying no intermediary stores your money. Instead, blockchain technology distributes assets across a network of nodes (computers). This makes all cryptocurrency activities, including public keys and transaction details, accessible to any interested party.
Though blockchain transactions occur in the public eye, they are anonymous. Decentralized applications (dApps) don’t request personal information, like your name, address, phone number, or passport number, to use. Instead, they assign you a private key to help you identify with your account.
A complex algorithm creates a public key from a private key, making them a pair. The private key confirms that the individual interacting with the public key is the real owner and can authorize transactions. As such, a private key secures crypto transactions by demonstrating ownership.
Private keys have their advantages and disadvantages. On the positive side, they guarantee a high level of security for crypto transactions. Considering their extensive length, it takes years to crack a private key. Besides, it’s faster and more convenient to perform private key encryption on the blockchain.
Nevertheless, private keys are prone to be lost. If you lose your private key, you won’t be able to decrypt the data you receive in your public key. This means you won’t access the assets in your wallet! Furthermore, if you keep your private key carelessly, it may fall into bad hands, and you may lose assets if that person has ill intentions.
How to Store Your Private keys
It’s important to store your private keys safely so they can’t easily get lost or stolen. Luckily, there are several ways to securely keep your private keys, which are classified into two broad groups:
Storing Them in an Online/Hot Wallet
This is the simplest and cheapest way of storing your private keys. Online wallets, commonly referred to as hot wallets, store your private keys on the internet. That makes it easy to use them but exposes them to online attacks. You should go for a hot wallet provider with a good reputation, a long track record of security, and reinforced with extra features, like two-factor authentication (2FA).
Storing Them in an Offline/Cold Wallet
The second way of storing private keys is offline or cold wallets. These wallets are either hardware insertable into computers or printable pieces of paper. Since these devices stay offline (unless connected during use), they prevent the digital theft of your private keys. But they are also prone to physical theft, damages, misplacement, and memory loss.
Generally, hot wallets are more convenient to use and often free. The common hot wallets include MetaMask, Trust Wallet, and Coinbase Wallet. On the other hand, cold wallets are often more secure as they mostly live offline but cost money. The common cold wallets include Trezor, Ledger, and KeepKey.
What are Public Keys?
A public key is an extensive string of characters used to encrypt information in cryptocurrency. It can be generated by a software program or assigned by a trusted crypto wallet provider. Any blockchain user can access and view the transactions of your public key through a blockchain explorer like Etherscan.
Besides, you can use a public key to encrypt a message or verify the validity of a digital signature. As mentioned, a public key is always accompanied by a matching private key, which the owner exclusively accesses. You need a private key to decrypt messages sent by the conforming public key or to produce signatures. In the simplest words, a public key locks up information from unauthorized access, while a private key unlocks it.
Public and private keys are the core of public key cryptography, often referred to as asymmetric cryptography. In this technique, each public key conforms with one private key. Crypto users need both keys to encrypt and decrypt messages – if you encrypt a message using someone’s public key, they can only decrypt it using the compatible private key.
For example, if Bob wants to send Alice an encrypted message, he will take Alice’s public key and encode his message to her. When the message is relayed to Alice, she uses her private key to decode Bob’s message.
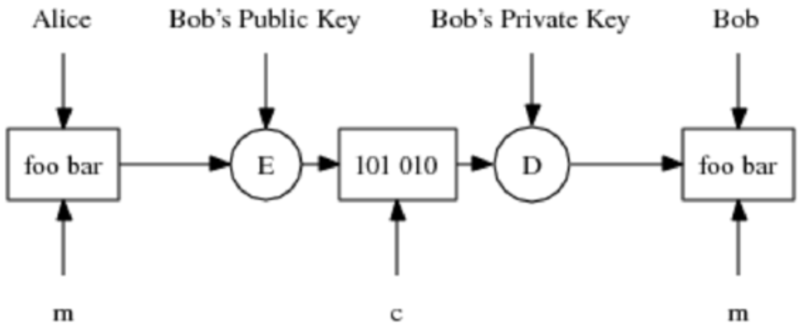
Source: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Alice-sends-an-encrypted-message-to-Bob_fig1_267544968
While bad actors might attempt to compromise the system and decode the message, they won’t succeed since they don’t have the private key that gives access. Only Alice can access the message since she is the only person with the private key. Besides, if Alice wants to respond, she repeats the process, encoding her message to Bob using his public key.
Differences Between Public Keys and Private Keys
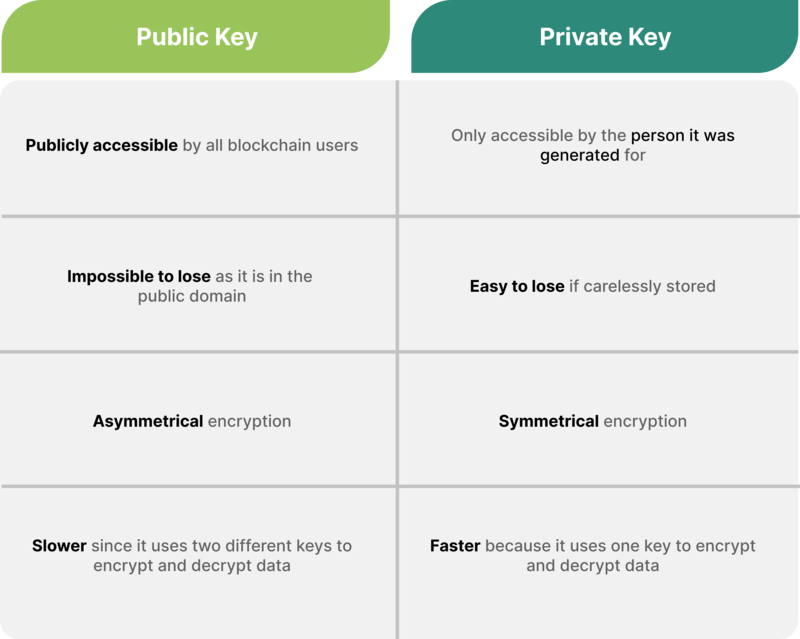
A public key can be accessed by any blockchain user and is used to send messages or funds, while a private key is exclusive to the person it was generated for and guarantees access to the sent message or funds. Together, these keys secure the shared data. These are the major differences between public keys and private keys:
Conclusion
Data storage and security are increasingly becoming integral as the world goes digital. Public key cryptography adds an extra security layer to data since nobody knows the private key paired with the open public key. As such, the technique mitigates potential interceptions and other online attacks. However, you must store your private key in a secure place where it cannot be easily lost or stolen.

