What Is a Bitcoin Wallet Address?
A Bitcoin wallet address is a long string of alphanumeric characters that acts as a unique identifier for sending and receiving Bitcoin. A similar analogy is that it is used much like an email address or personal bank account number.
Key Takeaways
-
A Bitcoin wallet address is a unique identifier used to send and receive Bitcoin much like how email addresses and bank account numbers are used.
-
A Bitcoin address is derived from a secret Private Key, which itself is generated from a master Seed Phrase. A single seed phrase can create a nearly infinite number of Bitcoin addresses.
-
Bitcoin addresses have evolved over the years for improved efficiency and new features, there are currently three types of Bitcoin addresses: Legacy, SegWit and Taproot.
-
You may search up Bitcoin addresses on Block Explorers, allowing you to view the address’s transaction history, total holdings and more.

How Is a Bitcoin Address Generated?
A Bitcoin address is created through a secure, multi-step process. The easiest way to understand it is in three steps, starting from the Seed Phrase.
Step 1: The Seed Phrase
The Seed Phrase is your master password, typically represented as a randomized list of 12 to 24 words selected from the BIP39 word list. This single phrase acts as the ultimate backup and is used to generate all of your keys.
In the early days, securing a seed phrase meant scribbling the wallet-generated words onto pieces of paper or storing them in insecure text files on PCs. This is where stories of lost Bitcoins worth billions come from.
These days, crypto wallets are able to automatically randomize and select words for you when you want to create a new Bitcoin wallet. Investors can also store and secure their seed phrase by storing them on pieces of steel using tools such as a Cryptosteel.
Step 2: The Private Key
A Private Key is a secret code that acts as the password for one Bitcoin wallet address. From the Seed Phrase, your wallet can generate a nearly infinite number of individual private keys.
Intuitively, this means you can have multiple Bitcoin wallet addresses generated from one single seed phrase, but each wallet address is secured by their own individual private keys.
Step 3: The Public Keys
For every private key, the wallet generates a corresponding public key. This public key is used to create the final, shareable Bitcoin address. This creates the familiar string of characters you see and share.
It is perfectly safe to share your public Bitcoin address to receive funds; it is your private key and seed phrase that must never be shared with anyone under any circumstances.
Your crypto wallet (like Ledger or Trust Wallet) is simply the tool that handles this entire process automatically. It securely stores your master seed and private keys, and generates the new addresses you need.
What Are the Different Types of Bitcoin Addresses?
Over the years, the Bitcoin network has been upgraded to improve efficiency, lower transaction fees, and add new capabilities like enhanced privacy. These upgrades introduced different address formats, with the main types being Legacy, SegWit, and Taproot.
Legacy (P2PKH) Addresses
-
Identifier: Starts with the number 1
-
Example: 1A1zP1eP5QGefi2DMPTfTL5SLmv7DivfNa
When Bitcoin first launched, this was the only type of address, now simply called Legacy. Its technical name is P2PKH (Pay-to-Public-Key-Hash), which describes the underlying method used for transactions.
P2PKH is an inefficient method of receiving/sending Bitcoins. Transactions using these addresses are the most expensive in terms of fees. Because of this higher cost, they are rarely used by most people today.
Segregated Witness (SegWit)
As Bitcoin grew more popular, the network became congested, leading to slower transactions and higher fees. In 2017, a major upgrade called Segregated Witness (SegWit) was introduced to make transactions more efficient and cheaper. This upgrade created two new types of addresses.
Nested SegWit (P2SH)
-
Identifier: Starts with the number 3
-
Example: 3J98t1WpEZ73CNmQviecrnyiWrnqRhWNLy
This was the first iteration of a SegWit Bitcoin wallet address, designed to be backwards compatible with existing wallets, allowing users to benefit from the cost savings of SegWit wallets without waiting for other Legacy wallets to adopt this new wallet standard.
Native SegWit (Bech32)
-
Identifier: Starts with bc1q
-
Example: bc1qf2kdgu2vlctqlnlxk4smkxd68grl5q2we8dzfd
This is the “true” and most modern form of SegWit address. It is the most efficient and preferred address type for most transactions today. Native SegWit has compatibility issues with Legacy wallets but in exchange, they are the cheapest to use, and have other benefits such as being easier to read and with better typo protection.
Taproot Addresses
-
Identifier: Starts with bc1p
-
Example: bc1pmzfrwwndsqmk5yh69yjr5lfgfg4ev8c0tsc06e
Activated in late 2021, Taproot is the newest upgrade to Bitcoin addresses. Its primary focus is on improving privacy.
The main benefit of Taproot is that it makes complex multi signature transactions look the same as single-signature payments. This makes it much harder for outsiders to analyze transactions, providing a significant privacy boost for all users. It is also more efficient for these complex transactions and has enabled recent innovations on Bitcoin like Ordinals and Runes.
Bitcoin Address Types at a Glance
This table provides a quick reference to summarize the key differences between the major Bitcoin address formats.
|
Feature |
Legacy (P2PKH) |
Nested SegWit (P2SH) |
Native SegWit (Bech32) |
Taproot (P2TR) |
|
Starts With |
1 |
3 |
bc1q |
bc1p |
|
Primary Benefit |
Universal Compatibility |
Backward Compatibility, Multi-sig |
Lowest Fees & Efficiency |
Enhanced Privacy & Flexibility |
|
Transaction Fees |
Highest |
Medium |
Lowest (for simple txs) |
Low (especially for complex txs) |
|
Best For |
Interacting with very old wallets or services. |
Sending to wallets that don’t support Native SegWit |
Most everyday transactions; saving on fees. |
Advanced multi-sig, and privacy-conscious users. |
How to Find and Use Your Bitcoin Address
Let’s move on to the practical steps of finding and using your Bitcoin address. The process is straightforward and is handled by your wallet software. Whether you are using a mobile wallet, desktop software, or a hardware wallet interface like Ledger Live, the steps are generally the same. Below we will go through two examples, Exodus and Ledger Live.
Exodus is a hot wallet, meaning it is a software wallet that stores your private keys in your computer while the Ledger is a cold wallet, which has the added security of storing your private keys in a hardware wallet not connected to the internet. These two examples should universally cover most of your needs whether it be a quick and relatively secure solution like a hot wallet or the added security of a cold wallet.
Finding Your Address on Ledger Live
-
Install Ledger Live and connect your Ledger Wallet.
-
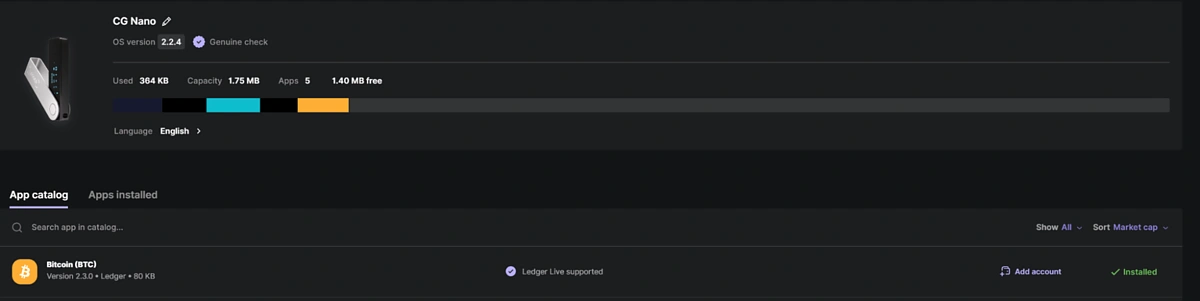
Head to “My Ledger” and install the Bitcoin application.
-
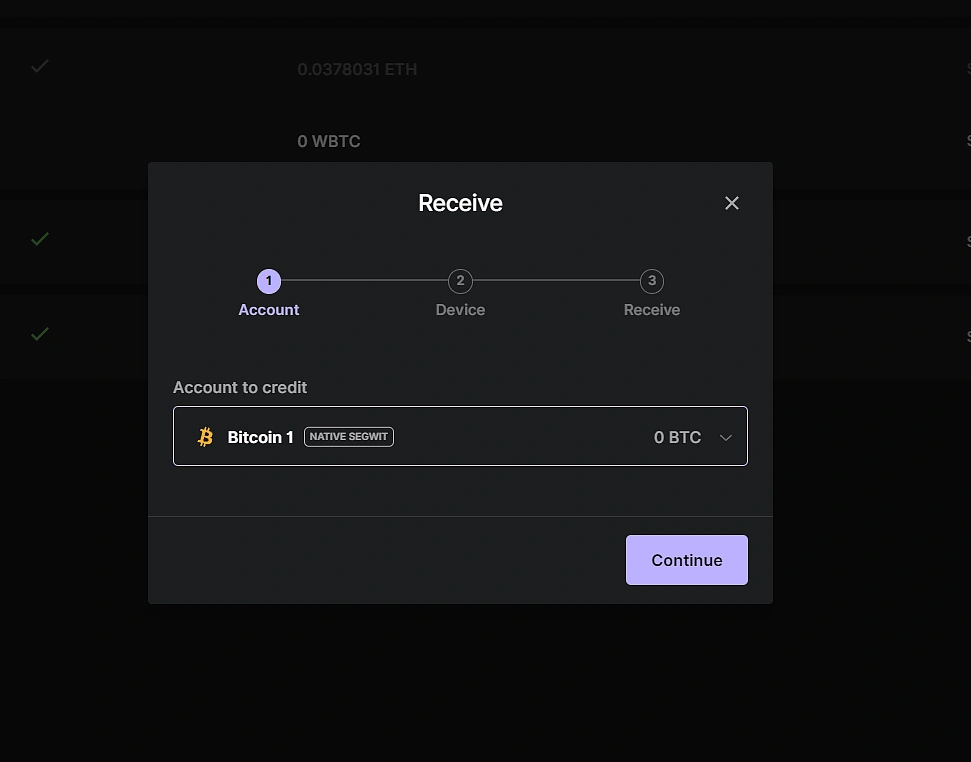
Go to “Receive” on the left sidebar and open the Bitcoin application.
-
Search “Bitcoin” and choose your desired Bitcoin address type. You may choose between Native Segwit and Taproot.
-
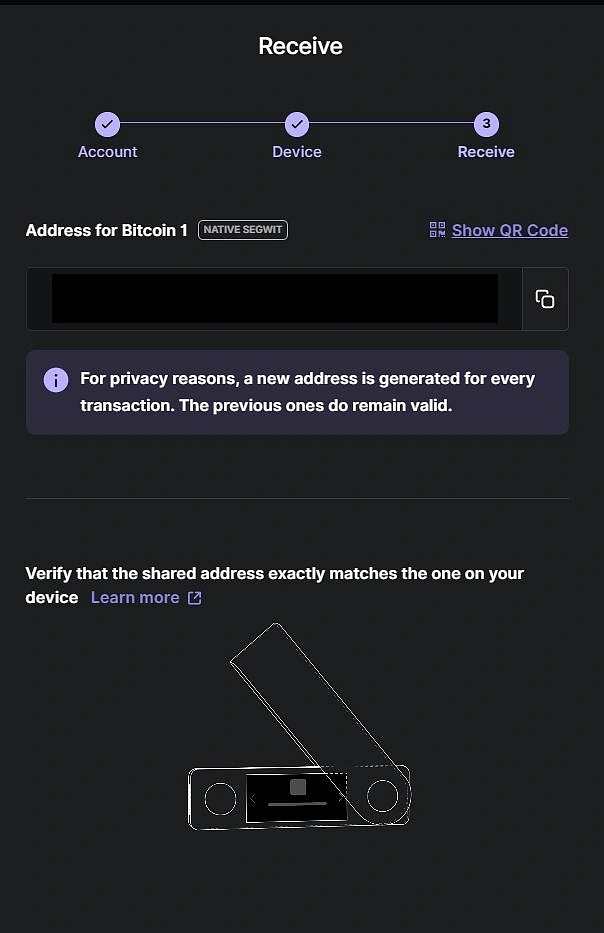
Confirm your address!
This is the last step, after confirming your address feel free to copy and paste your address to use them in transactions or to use the QR code.
Finding Your Address on Exodus
-
Go to https://www.exodus.com/download to download and install the wallet.
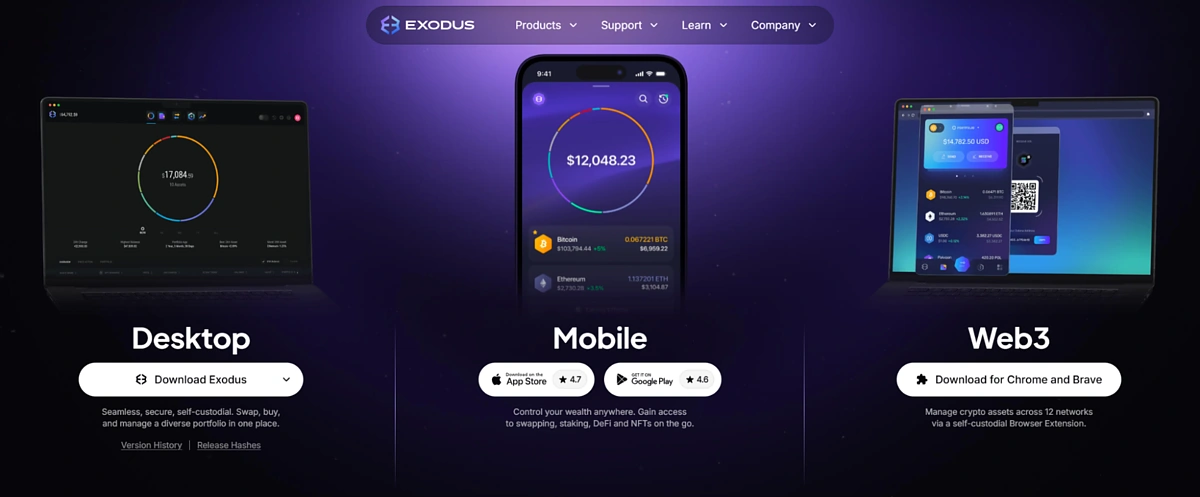
Exodus offers a desktop app, mobile app, and browser extension. In light of Bitcoin’s growth in DeFi and Layer 2s, this guide will focus on the browser extension, as it is the primary tool for interacting with these applications.
-
Install and add the Chrome extension
-
Click the extension (at the top right), which will redirect you to create a new wallet or import an existing wallet.
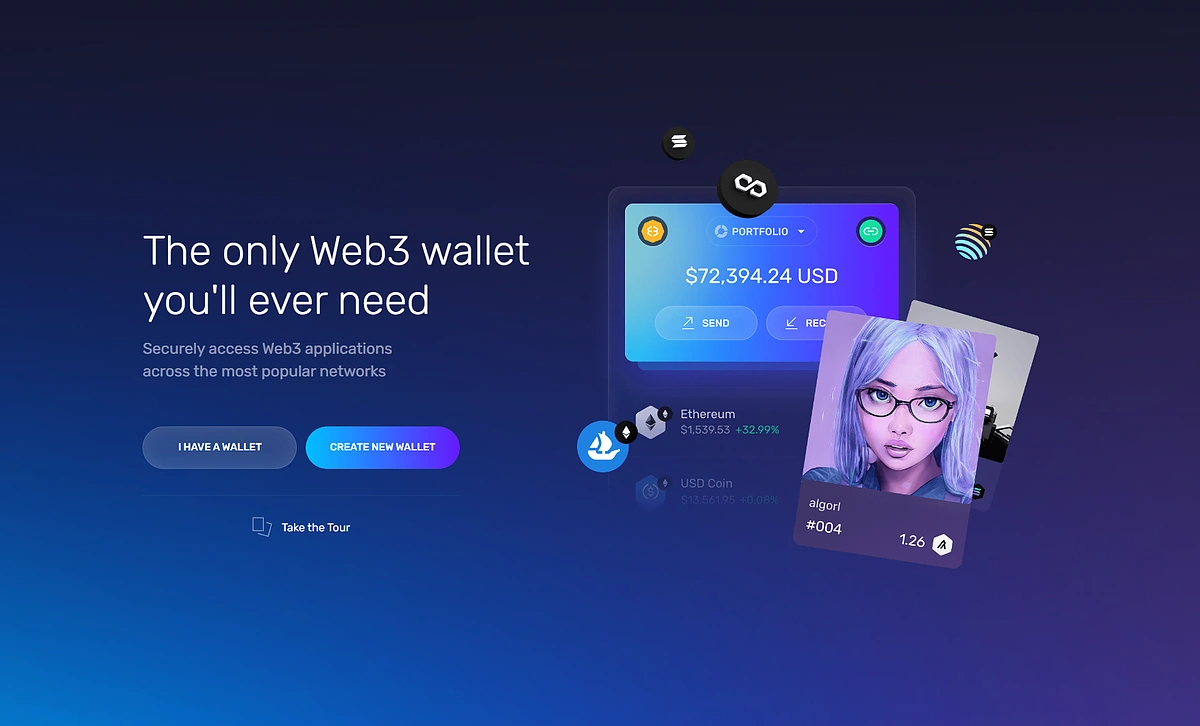 Follow the instructions and complete your wallet set up.
Follow the instructions and complete your wallet set up.
-
Select the wallet symbol at the bottom.
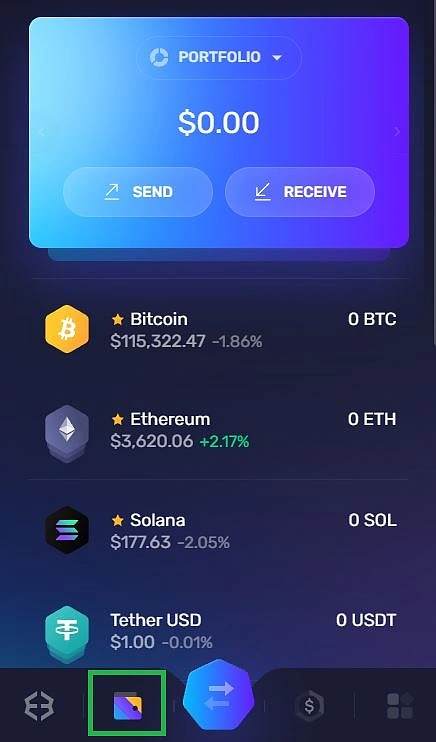
-
Select receive and click Bitcoin.
That’s it! You can now see your address which can be shared in order for you to receive Bitcoin.

Sending and Receiving Bitcoin
Now, let’s look at how you can send and receive Bitcoin with your wallets.
Sending and Receiving On Ledger Live
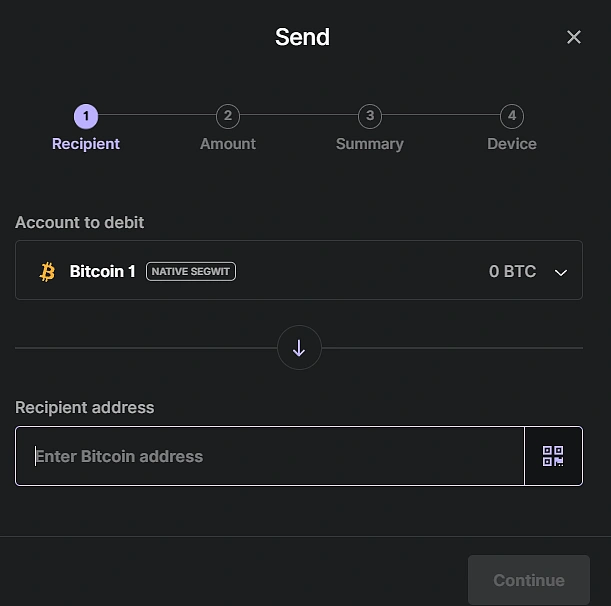
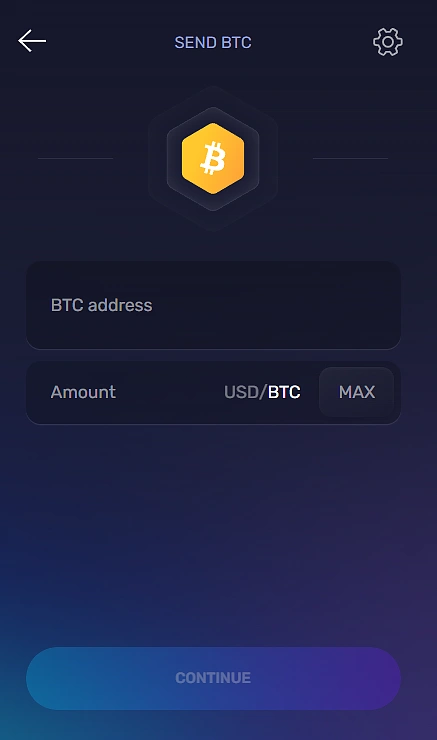
Sending and Receiving On Exodus
You can receive Bitcoins by sharing your address found in step 5. To send Bitcoin, return to the Exodus menu in step 4 and hit “Send”. This will bring you a menu to send your Bitcoins to your desired Bitcoin address.
How to View Bitcoin Transaction Records
After sending your Bitcoins, your transaction is forever recorded on the Bitcoin blockchain. You can view them and see the status of your transaction using something called a blockchain explorer.
Blockchain Explorers
A blockchain explorer is best described as a “search engine for a blockchain”. It is a website or application that allows you to browse and search all of the public data on the specified blockchain network, including every transaction, address, and block ever created.
Mempool.space is a popular and user-friendly blockchain explorer for the Bitcoin network. Blockchain explorers are useful for users to be able to verify their transaction status, check historical transactions and even trace funds!
How to Use a Blockchain Explorer
In this section, we’ll go through an example of how to use Mempool.space
Mempool’s Homepage
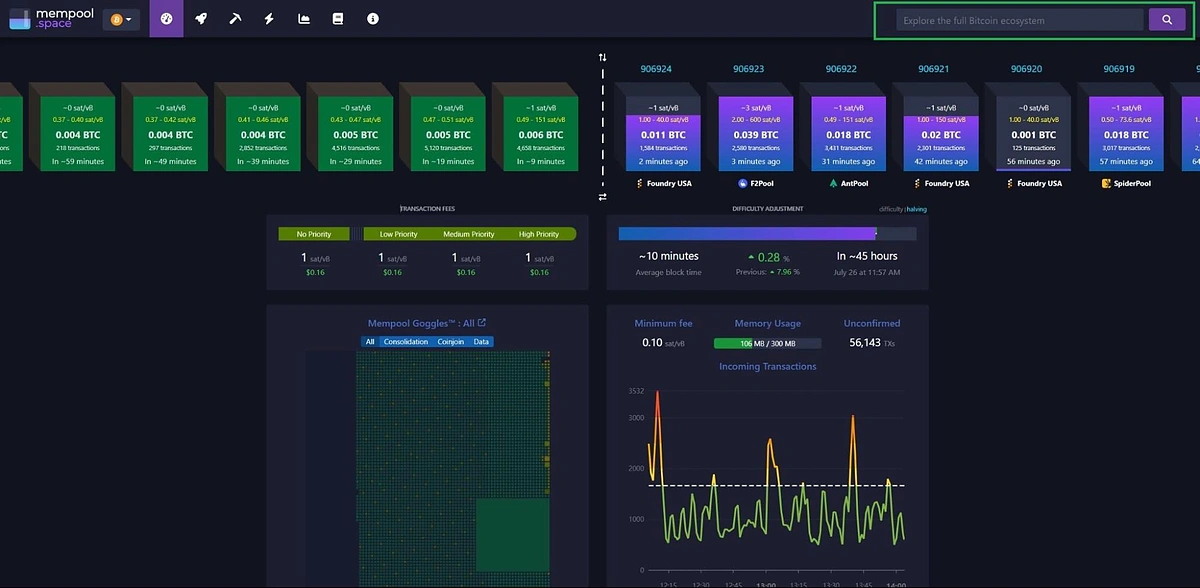
The homepage of Mempool contains useful information about the status of the Bitcoin blockchain. Information such as network status, network activity and average transaction fees are displayed here! The search bar to look up your desired Bitcoin address is located in the top right corner.
How to Look Up a Bitcoin Address
For this example, we will take a look at 1A1zP1eP5QGefi2DMPTfTL5SLmv7DivfNa, widely believed to be one of Satoshi Nakamoto’s many Bitcoin addresses.
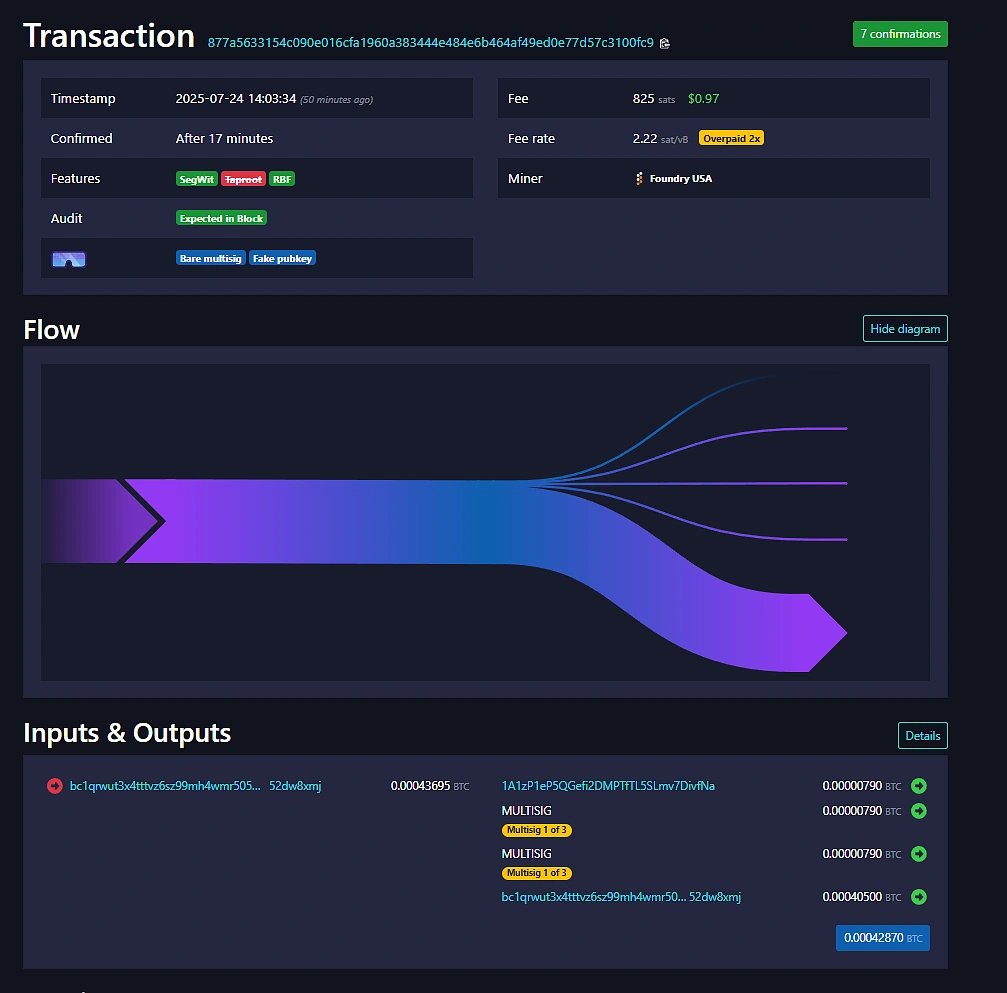
The above is a menu of what you will see after searching up a Bitcoin address, at the top of you will see basic information such as the total amount of Bitcoin holdings, its associated value in dollars as well as its address type, which in this case is P2PKH, or Legacy.
From the balance history, you can see that Satoshi’s Bitcoin balances have been steadily increasing till this day. This is initially surprising because we know that Satoshi Nakamoto is no longer publicly active in the crypto space. However, this can be explained when you look at the transaction history at the bottom. You can see that this Bitcoin wallet address has been receiving small amounts of Bitcoin from random Bitcoin addresses even till today. While the exact reasons vary, people often do this to pay homage to Satoshi, to test new services, or simply to link their own transaction to a historic address. This explains why the balance continues to grow over time.
Individual Transaction Details
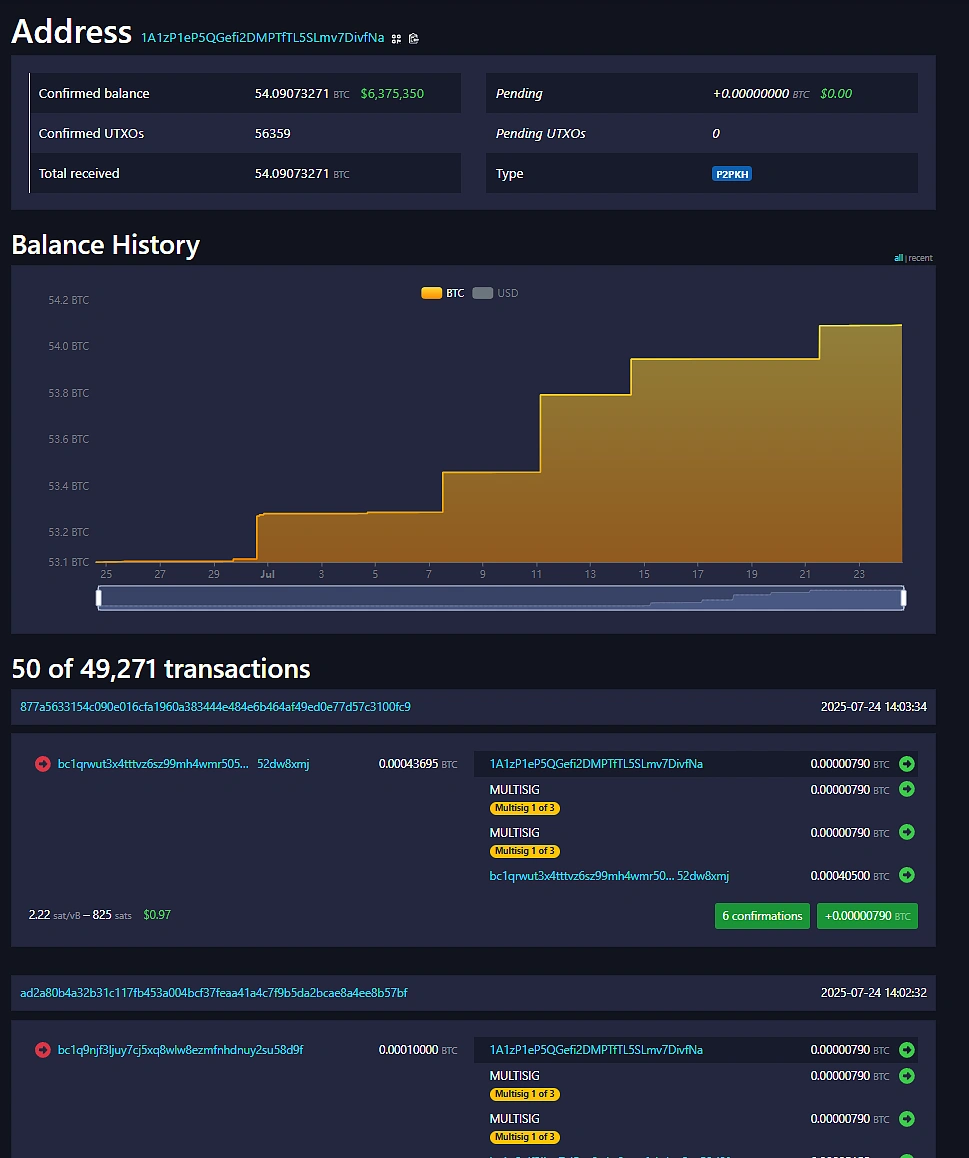
Taking a closer look at one of those transactions to Satoshi we see that it is from a relatively modern wallet, as evidenced from its Native Segwit status. We can also see when the transaction was made, how long it took to confirm (17 minutes), how much fees the sender paid for the transaction to go through and which miner validated this transaction (Foundry USA).
As a sidenote, you may also search up individual transactions directly instead of first searching up the Bitcoin address. Each Bitcoin transaction has an TXID, “877a…” in this case, which you can use on the search bar at the homepage of Mempool.
This single example shows how much information is available on the blockchain. And that’s the gist of operating a block explorer and how you can use it!
Address Privacy and Security
By now, we can see how easy it is to track holdings and view exactly how much funds a specific wallet address holds. Thankfully, crypto wallet addresses are pseudonymous and do not reveal your identity in any way. However, this is where user error and carelessness can breed a new kind of risk where you leak your public wallet address online in a manner that can be traced back to your real physical identity.
Although it is cryptographically secure to share your public wallet address, this is dangerous because of the rise of “wrench attacks”. Wrench attacks refer to physical attacks or robberies that target high-value crypto wallet address holders and their close friends and families. Targets typically include well known crypto influencers (KOLs), crypto founders and overall careless individuals.The best way to protect yourself is to never publicly associate addresses that hold significant funds with your personal identity. This is also why privacy-enhancing technologies like Taproot addresses and tools like crypto mixers are so important to the crypto ecosystem.
Conclusion
Understanding a Bitcoin address is the first step toward confidently navigating the world of crypto. It is far more than just a random string of characters, it is your personal, publicly-shareable address on a globally decentralized and permissionless financial network.
If there is one core principle to take away, it is the clear distinction between what is public and what is private. Your Bitcoin address is for sharing, your private key is for securing. Keep your seed phrase safe and do not share it under any circumstance except for use in recovering or setting up new wallets! Grasping this simple but powerful concept is the foundation for safely and effectively participating in the Bitcoin economy.
This article is for educational and informational purposes only and should not be considered financial or investment advice. The cryptocurrency market is highly volatile, and you should conduct your own research and consult with a qualified professional before making any financial decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Do I Need to Change my Legacy Address?
No you don’t have to. However, if you are using your Legacy wallet using older wallet software, it may not be able to recognise newer address types such as Native SegWit and Taproot, which can be a pain point for you. You are also paying higher transaction fees using a Legacy wallet. So while you don’t have to “change” your Legacy address, it is still generally recommended you retire the Legacy wallet and use a more modern wallet, utilizing the more efficient Native SegWit address type.
Can I Reuse a Bitcoin Address?
You can, but it’s strongly recommended that you do not for privacy reasons. To make good privacy easy and practical, modern wallets automatically provide a fresh, new address every time you want to receive a payment. You should always use this new address. However, users who use DeFi services on Bitcoin Layer 2s generally ignore this advice because it is highly impractical to use disposable addresses in DeFi.
How Many Bitcoin Addresses Can I Have?
As many as you want!
What Happens When I Send Bitcoin to a Wrong Address Type?
Usually, nothing bad will happen. Modern wallets can send funds to any address type (Legacy, SegWit, Taproot) without any issues. The only problem you might encounter is if you try to use a very old, non-updated wallet to send to a new address format (like Taproot). The old wallet may not recognize the format and give you an “Invalid Address” error, which simply prevents you from sending the transaction.
Is My Bitcoin Address Case-Sensitive?
Legacy and Nested SegWit addresses are case-sensitive. Native SegWit and Taproot addresses are not case-sensitive.
What Happens When I Lose My Password?
If you lose the password to your Exodus wallet or the PIN to your hardware wallet, you are still able to restore the wallet through your Seed Phrase. Your Seed Phrase however, cannot be restored if you lose it.
Can Someone Guess My Seed Phrase?
No. The number of possible combinations for a 12-word seed phrase is so astronomically large that it is mathematically impossible for anyone to guess it. It can, however, be stolen from you through phishing attacks, malware, or by someone physically finding where you’ve written it down.
