What Gives Bitcoin Value?
Bitcoin’s value comes from its limited supply and growing demand. Only 21 million bitcoins will ever exist, and fewer are made each year, making it scarce like gold. More people and institutions want to use it as a way to store value, driving up its price compared to regular money.
Key Takeaways
-
Bitcoin has a hard cap of 21 million, making it resistant to inflation. This programmed scarcity drives up the value.
-
No single entity controls Bitcoin; it’s run by a global network.
-
Bitcoin is protected by the world’s most powerful computing network via Proof of Work.
-
Institutional, corporate, and even nation-state interests have legitimized Bitcoin.
-
Despite thousands of altcoins, Bitcoin’s durability and simplicity keep it dominant.

‘People are paying real money, and in millions, to buy magic internet money!?’ That’s usually the first reaction by the uninitiated when they hear about Bitcoin.
For decades, people (in general) associated value with tangibility. If they can see it and feel it, they can pay for it justifiably. Even currency was backed by physical gold in banks, and even after the US abandoned the gold standard, people could still get ‘physical cash’ in their hands and know for a fact that it is real.
Hence, skepticism around Bitcoin’s value is understandable. If you can’t hold it, see it, or spend it at a grocery store, can it still be worth something? Bitcoin isn’t backed by gold, is not controlled by a government, and doesn’t even exist in physical form. Yet, it is now shaping global economies! So what gives Bitcoin its value?
Where Does BTC Get Its Value From?
Bitcoin’s value boils down to supply-demand dynamics. BTC supply is capped at 21 million, and the rate of BTC production is also decreasing every four years due to Bitcoin Halving. The demand (from popularity and utility), however, is growing. This growing demand and shrinking supply contribute to Bitcoin’s value compared to fiat currency.
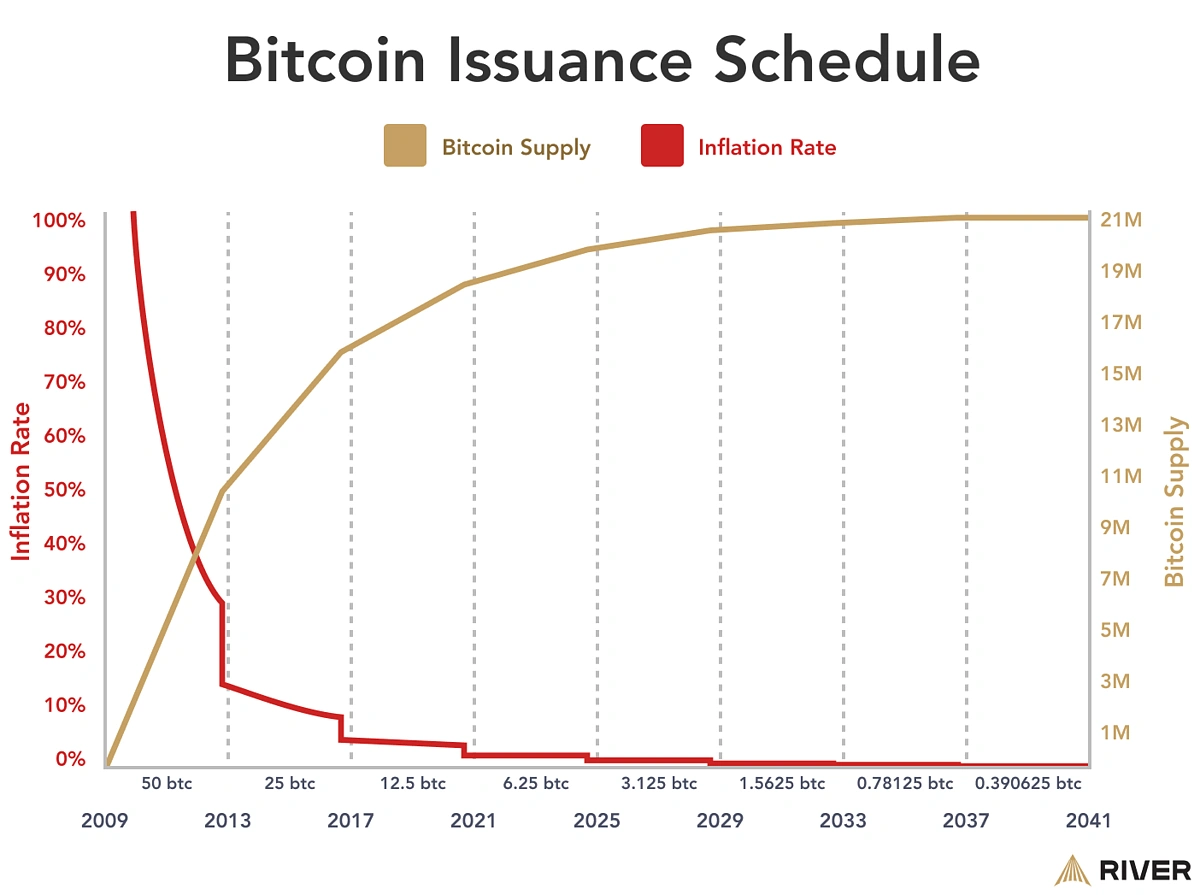
Simply put, Bitcoin’s value comes mainly from its programmed scarcity.
Bitcoin’s programmed scarcity is partly due to its use of Proof of Work. Bitcoin’s Proof of Work is like a global lottery where miners buy “tickets” with computational power to win the prize of new bitcoin. The difficulty adjusts to ensure a winner is found roughly every 10 minutes, just like how a lottery might adjust ticket prices to maintain consistent drawings.
Bitcoin’s network effect works like the first telephone networks: one telephone was useless, but every telephone became more valuable each time someone new joined the network. Bitcoin follows the same principle – each new user, merchant, or institution joining the ecosystem makes the entire network more valuable for everyone.
Digging deeper, there are six factors contributing to Bitcoin’s value:
-
Scarcity
-
Decentralization
-
Security
-
Utility
-
Network effects
-
Belief and trust
1. Scarcity: There Will Only Ever Be 21 Million
Bitcoin is scarce by design. Similar to resources like gold, Bitcoin, too, is finite. In fact, humans could find new deposits of gold, but would never find “new Bitcoin” because the scarcity is defined in its source code. There will only ever be 21 million BTC, and no one, not even the creator, can change that.
Every 10 minutes, new BTC is created through a process called mining, but the rate of creation slows down over time. Roughly every four years, the number of new bitcoins that can be mined gets cut in half. This means Bitcoin becomes harder and harder to produce as time goes on.
This built-in scarcity makes Bitcoin resistant to inflation, unlike fiat currencies (like dollars or euros) that can be printed in unlimited quantities.
2. Decentralization: No One Controls It
Unlike fiat money, Bitcoin isn’t issued by a central bank. It’s maintained by a network of computers, called nodes, that are spread worldwide.
Taking it a step further, the transaction validation and consensus happen in a trustless fashion. That means, there are no dependencies on intermediaries to ensure fair play – everything is governed by code and cryptographic primitives.
So, no single government, corporation, or individual can shut down the network, freeze funds, or change rules in self-interest. This decentralized nature gives users confidence that Bitcoin is fair, transparent, and immune to the kinds of manipulation that have affected traditional currencies.
You also don’t need permission from anyone to use Bitcoin. That’s what makes it open and global.
3. Security: Protected by Proof of Work
Bitcoin is incredibly secure thanks to “Proof of Work”. Every transaction is verified and added to the blockchain through complex mathematical puzzles that require vast amounts of computing power to solve.
This process is done by miners in exchange for BTC as a reward. Together, these computers (miners) form the most powerful computing network in the world.
What does this mean in practice? Once your transaction is confirmed, it’s irreversible, tamper-proof, and public for anyone to verify. That level of transparency and integrity gives users confidence in the system.
4. Utility: Bitcoin Is Great For Payments
Bitcoin is a functional currency and financial tool that enables several real-world use cases similar to fiat money (but better).
Remittances and cross-border money transfers are a huge use case of BTC. Bitcoin lets anyone transfer value (from pennies to billions) across the world within minutes. For example, in 2020, a Bitcoin user transferred $1 billion at a meagre fee of just $3!
For microtransactions, like going to a nearby store and paying for bread, waiting 10 minutes and paying a couple of dollars for a dollar’s worth of bread is impractical. In such cases, people can use Lightning Network and other Bitcoin Layer 2s, which are built atop Bitcoin to power low-cost, ultra-fast payments.
In a world of increasing financial surveillance and restrictions, Bitcoin offers freedom to move money on your own terms.
Bitcoin vs. Gold. vs. US Dollar
To understand why Bitcoin has value, let’s examine it through the lens of classical monetary theory. Economists have long identified six key properties that make for effective money: scarcity, divisibility, portability, durability, uniformity, and acceptability.
Property |
Bitcoin |
Gold |
US Dollar |
|
Scarcity |
✅ Excellent
Hard cap of 21 million coins, mathematically enforced by code. No new supply can ever be created beyond this limit. |
⚠️ Good
Limited supply, but new gold can still be mined. Annual production ~3,000 tons, total above-ground stock ~200,000 tons. |
❌ Poor
Unlimited supply. The Federal Reserve can print money at will. M2 money supply increased 40% during 2020-2021. |
|
Divisibility |
✅ Excellent
Divisible to 8 decimal places (100 million satoshis per bitcoin). Perfect for micro-transactions. |
❌ Poor
Physically difficult to divide into small units. Requires melting and reshaping, impractical for everyday use. |
✅ Excellent
Easily divisible into cents (100 cents per dollar) both physically and digitally. |
|
Portability |
✅ Excellent
Weightless and can be transmitted globally in minutes. $1 billion can be stored on a smartphone or memorized as a seed phrase. |
❌ Poor
Very heavy and bulky. $1 million in gold weighs ~50 pounds. Requires secure transportation and storage. |
⚠️ Good
Physical cash is portable for small amounts. Digital transfers are fast domestically but slow/restricted internationally. |
|
Durability |
✅ Excellent
Exists as immortal information on an immutable blockchain. Cannot be destroyed, corroded, or damaged. |
✅ Excellent
Does not corrode, tarnish, or decay. Maintains physical properties over thousands of years. |
❌ Poor
Physical cash degrades over time. Digital dollars lose purchasing power due to inflation (3-4% annually average). |
|
Uniformity |
⚠️ Good
Each bitcoin is identical in the protocol, but the transaction history is public, potentially affecting fungibility. |
⚠️ Good
Gold purity varies (different karats), but standardized forms like bars and coins achieve good uniformity. |
✅ Excellent
Each dollar bill has identical value and acceptability regardless of serial number or physical condition. |
|
Acceptability |
⚠️ Good & Growing
Accepted by major corporations (Tesla, Microsoft), payment processors (PayPal, Stripe), and some governments. Growing rapidly. |
⚠️ Good
Universally recognized store of value and is accepted by central banks. Limited use for daily transactions. |
✅ Excellent
Global reserve currency, accepted worldwide for trade, and required for US tax payments (drives demand). |
5. Network Effects: The More People Use It, the More Valuable It Becomes
Bitcoin gets stronger the more people adopt it. This is called a network effect. The more users, merchants, wallets, exchanges, and institutions that accept Bitcoin, the more useful it becomes, and the more people want to own it.
This phenomenon is often described by Metcalfe’s Law, which states that a network’s value is proportional to the square of the number of its users or nodes. That’s math-speak for each new user multiplies the value of the network.
For example, say Bitcoin has 10 users. Let’s give it a value of 100. Now, if it had 100 users, its value would jump to 10,000.
This is similar to how email or the internet became more valuable as more people came online.
With more holders and merchants, Bitcoin becomes more practical. More exchanges list it, and more businesses accept it for payments. The chances that you can use your BTC for something are much higher now than a decade ago, and each new wave of adoption also legitimizes Bitcoin further in the eyes of the public.
6. Belief and Trust: The Social Consensus Behind Money
At the end of the day, money is a shared belief system. A $100 bill only works because we all agree it has value. Bitcoin is no different. Its value comes from the global consensus that it’s scarce, secure, useful, and credible.
Over time, this belief has been reinforced by adoption from major financial institutions, corporations, and even countries. That growing trust adds weight to Bitcoin’s reputation and helps explain why people are willing to exchange real goods and services for it.
Institutional Adoption Propelled Bitcoin Into the Mainstream
While Bitcoin’s value grew exponentially in the trenches of web3 and deepweb, its adoption by institutions (from BlackRock to Strategy) is what pushed it way past the $100k-mark.
Bitcoin Became A Safe Haven For Corporates
At times of economic uncertainty and high inflation, Bitcoin’s fixed 21 million supply started to look less like a quirk and more like a feature. That’s when corporate treasuries started buying Bitcoin. Strategy (formerly MicroStrategy) led the way in 2020, converting over $1 billion of its cash reserves into BTC.
Large financial players, corporations, and investment firms integrating cryptocurrency into their operations legitimized Bitcoin and unlocked massive pools of capital.
ETF Approvals Opened Retail Money Gates
One of the most impactful moments came with the approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs (these allow people to invest in BTC through regulated stock markets). This dramatically lowered the entry barrier for retail money to flow into BTC. Now, Bitcoin could even be part of a 401(k) or pension fund of the elderly who barely know how to operate a smartphone, much less navigate a Bitcoin wallet.
Bitcoin on the Balance Sheets of Nations
Perhaps the most profound signal of Bitcoin’s institutional rise is nation-state adoption.
In 2021, El Salvador became the first country to declare Bitcoin legal tender, integrating it into public infrastructure, tourism, and remittances. Since then:
-
The Central African Republic followed with its own Bitcoin initiative
-
Bhutan quietly mined Bitcoin using renewable energy
-
Ukraine accepted Bitcoin donations during wartime
-
Argentina and Venezuela saw surging citizen-level Bitcoin use to escape currency collapse.
While not every country has made it legal tender, strategic Bitcoin reserves have become the talk of the town.
A strategic Bitcoin reserve is a small allocation of BTC held by central banks or sovereign funds as a hedge against inflation and protection from international currency dominance.
Why BTC? Because Bitcoin is the first truly global, non-sovereign asset that is borderless like the internet, yet scarce like gold, which no single nation can control.
Beyond the balance sheets of nations, real-world issues are also driving Bitcoin adoption, even in countries that may limit use.
Hyperinflation Protection: In Argentina, where inflation exceeded 100% annually, citizens turn to Bitcoin to preserve purchasing power.
Capital Flight Prevention: In countries with strict capital controls, Bitcoin provides an escape valve for wealth preservation.
Sanctions Resistance: For nations facing international sanctions, Bitcoin offers an alternative to the dollar-dominated global financial system.
Monetary Sovereignty: Even stable nations recognize the strategic value of holding an asset independent of any other country’s monetary policy.
Is Bitcoin Backed By Anything?
One of the most common questions people ask about Bitcoin is, “But what’s it backed by?” Like we’ve established before, people are used to the notion that money needs to be backed by something tangible, like gold, silver, or the authority of a government.
The irony is, however, most money today isn’t backed by anything either.
Today, when you use a Dollar or a Euro, you’re trusting:
-
That the issuing government is stable
-
That the central bank will manage inflation
-
That others will accept the currency as payment.
So, the value of money has less to do with physical backing and more to do with belief, usage, and economic confidence.
Bitcoin may not have a bag of gold backing it, but it does have the backing of:
-
Cryptography and code that enforce rules unbiased
-
The world’s largest computational network that secures the chain
-
High economic incentives that align participants and promote fair play
-
Decentralized global consensus that maintains 100% uptime
-
A brilliant growth record compared to traditional finance products.
Does Competition From Altcoins Weaken Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is the first fully decentralized cryptocurrency. Since its birth, however, thousands of new cryptocurrencies have come up (ETH, SOL, ADA, XRP, etc.) to deliver on Bitcoin’s shortcomings. Some offer faster transactions, and others support smart contracts or enhanced privacy.
Logically, the rise of altcoins (coins other than Bitcoin) should have weakened Bitcoin’s stance in the market. But it only made the OG crypto much stronger, with BTC dominance on the rise 3 years in a row! There are two big reasons for this:
-
Altcoins are sandboxes
-
Altcoins come and go
Altcoin Sandboxes
Most altcoin projects have historically tried to achieve the same goal of solving the blockchain trilemma. A few others take specialized routes like:
-
Enabling complex P2P on-chain agreements (smart contracts by Ethereum)
-
Near real-time transactions (like Solana)
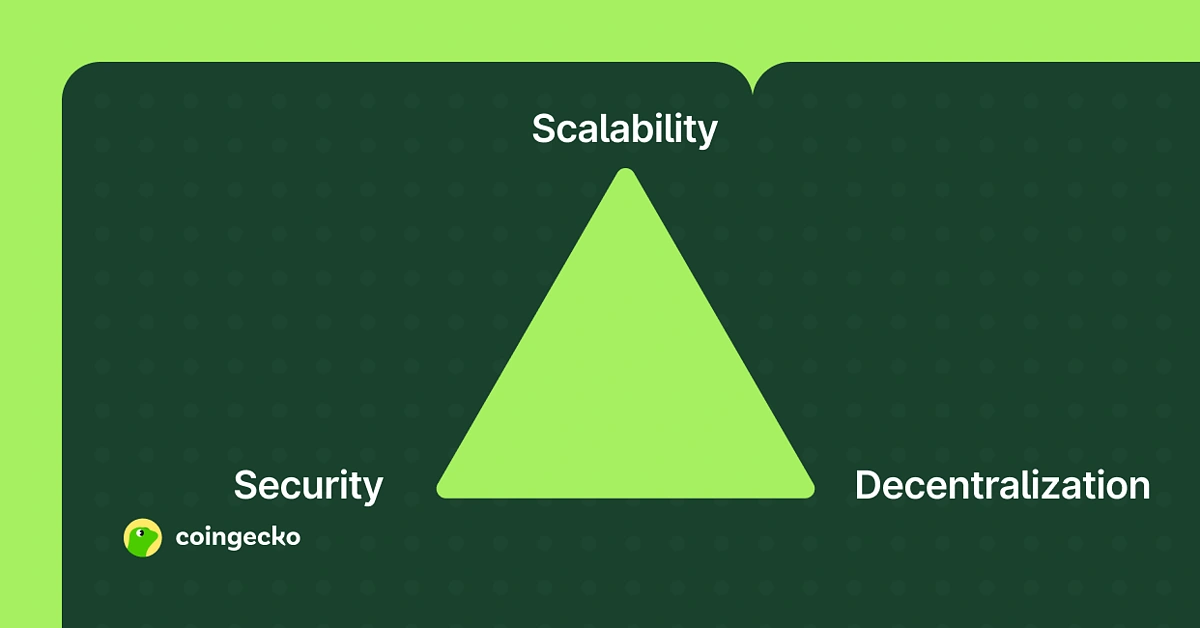
These experiments are important because they push the limits of what blockchains can do. But most of these innovations come with trade-offs that keep them from overthrowing Bitcoin.
Altcoin Graveyard
Many cryptocurrencies dubbed “Bitcoin killers” and “Ethereum killers” in 2017 barely make it to headlines in 2025. Projects come and go, tech trends fade, and communities move on. But through all of it, Bitcoin remains.
This long-term durability is known as the Lindy Effect (the longer something has survived, the more likely it is to continue surviving).
Common Questions & Misconceptions About Bitcoin’s Value
Let’s look at the most common criticisms and misconceptions about Bitcoin’s value:
“Bitcoin is just speculation – greater fool theory”
While speculation exists, Bitcoin has real utility as a payment system, store of value, and hedge against monetary debasement. The “greater fool theory” applies to assets with no underlying value, but Bitcoin provides genuine technological and economic benefits that traditional money cannot.
“Bitcoin is too volatile to have real value”
Volatility is a characteristic of emerging assets, not a disqualifier for value. The internet, smartphones, and electric cars were all volatile during their adoption phases. Bitcoin’s volatility has actually decreased significantly as the market has matured and institutional adoption has grown.
“Bitcoin transactions are too slow and expensive”
Bitcoin’s base layer prioritizes security and decentralization over speed. For everyday transactions, Layer 2 solutions like Lightning Network enable fast, low-cost payments. Think of Bitcoin like the international banking settlement layer, with Lightning as the payment processing layer.
“Bitcoin wastes too much energy”
Bitcoin’s energy use secures the world’s hardest money. Recent studies indicate Bitcoin mining operations are increasingly powered by renewable energy sources. This energy expenditure is a feature, not a bug – it’s what makes Bitcoin tamper-proof. The traditional banking system also consumes enormous energy when you include bank branches, ATMs, data centers, and armored trucks.
“Bitcoin has no intrinsic value”
Bitcoin’s “intrinsic value” comes from its monetary properties: scarcity, portability, divisibility, durability, and censorship resistance. These properties are coded into the protocol and maintained by the largest computational network in history.
“Government can just ban Bitcoin”
While governments can regulate Bitcoin, they cannot shut down the decentralized network. Countries that have attempted bans (like China) face enforcement challenges, with users employing workarounds like VPN usage and P2P trading. In fact, China is in the top 20 when it comes to Chainalysis’s 2024 global crypto adoption index.
Conclusion
Ultimately, what gives Bitcoin its value is the collective recognition of its utility and trustworthiness as a form of money that is independent of any one authority, scarce by design, secure to its core, and usable by anyone.
Bitcoin may not have a physical form, but in many ways it’s more real than fiat money, providing underserved users an alternative currency to store value.
