What Are Bitcoin Treasuries?
Bitcoin treasuries are reserves of Bitcoin held by companies, governments, or institutions as part of their financial strategy, typically to hedge against inflation, diversify assets, or gain exposure to Bitcoin’s potential upside. These holdings appear on their balance sheets, similar to cash or gold.
Key Takeaways
-
Bitcoin is replacing cash in corporate treasuries as inflation, low yields, and monetary uncertainty push companies to seek alternative stores of value.
-
MicroStrategy’s success has inspired over 180 companies across sectors like telecom, energy, and healthcare to adopt Bitcoin as a primary reserve asset.
-
Holding Bitcoin lets companies raise capital, attract investors, and outperform traditional assets.
-
New accounting rules and rising institutional acceptance are removing barriers for companies to actively manage Bitcoin treasuries transparently.
-
Despite benefits, Bitcoin treasuries face real challenges like regulatory uncertainty, audit limitations, custody risks, and potential capital erosion during price downturns.

The Rise of Bitcoin Corporate Treasuries
Bitcoin corporate treasuries are transforming how companies manage their cash reserves. Instead of holding only traditional assets like cash and bonds, an increasing number of companies worldwide are allocating portions of their balance sheets to Bitcoin as a strategic financial move.
What exactly is a Bitcoin corporate treasury? Simply put, it’s when a company holds Bitcoin on its balance sheet as part of its financial reserves, treating it like any other treasury asset such as cash, bonds, or commodities.
This is a fundamental shift in corporate finance. With rising inflation, shrinking bond yields, and growing uncertainty around monetary policy, over 180 companies worldwide have already adopted Bitcoin treasury strategies, led by pioneers like Strategy (formerly MicroStrategy), which holds over 600,000 BTC worth billions of dollars.
Understanding Bitcoin Treasuries
A “Bitcoin treasury” is the portion of an organization’s financial reserves that is held in Bitcoin.
Think of a corporate treasury as a company’s financial safety net (the money it keeps aside to pay bills, handle unexpected costs, or fund new projects during tough times). Traditionally, these treasuries consisted of ultra-safe assets: cash, short-term government bonds, and money market funds.
A Bitcoin corporate treasury takes this concept one step further by including Bitcoin as a reserve asset alongside (or instead of) these traditional holdings.
Key characteristics of Bitcoin corporate treasuries:
-
Bitcoin appears on the company’s balance sheet as an asset.
-
Holdings are typically meant for long-term value preservation, not trading.
-
Companies use Bitcoin to hedge against inflation and currency debasement.
-
The strategy requires specialized custody and security measures.
Unlike individual investors who might buy Bitcoin for speculation, companies adopting Bitcoin treasuries usually have strategic reasons: protecting against inflation, diversifying reserves, or gaining exposure to Bitcoin’s potential upside while maintaining operational liquidity.
Why Companies Are Adopting Bitcoin Corporate Treasuries
The shift toward Bitcoin treasuries is driven by several economic and strategic factors. A few of them are explained here.
1. Inflation Hedge and Currency Protection
Traditional cash holdings lose purchasing power during inflationary periods. With many countries experiencing sustained inflation, Bitcoin’s fixed supply of 21 million coins makes it attractive as a store of value. Unlike fiat currencies that central banks can print indefinitely, Bitcoin’s scarcity is mathematically guaranteed.
A McKinsey study reveals that 54 countries representing 93% of global GDP introduced $10 trillion in stimulus during COVID-19 (three times more than during the 2008 financial crisis). This massive money printing has companies seeking alternatives to preserve long-term value.
2. Superior Returns Potential
Bitcoin has historically outperformed traditional treasury assets by significant margins. While the S&P 500 delivered approximately 10% annual returns since 2009, Bitcoin has achieved over 200% compound annual growth rate since 2011, despite its volatility.
|
Asset |
Approx. Return |
Time Span |
CAGR (Annualized Return) |
|
Bitcoin |
~11.2M% (from $1) |
2011–2025 (~14y) |
~203% |
|
Amazon (AMZN) |
~200,000% |
1997–2021 (~24y) |
~37% |
|
Apple (AAPL) |
~135,000% |
1980–2021 (~41y) |
~26% |
|
Gold |
~600% |
1971–2021 (~50y) |
~4% |
|
S&P 500 Index |
~400% |
2009–2025 (~16y) |
~10% |
For companies with excess cash earning minimal returns in low-yield bonds or money market funds, Bitcoin presents an opportunity for meaningful capital appreciation.
3. Diversification and Liquidity
Bitcoin operates independently of traditional financial systems, providing 24/7 global liquidity. For multinational companies, Bitcoin can serve as a neutral currency for cross-border transactions and a hedge against any single country’s monetary policy decisions.
4. Access to Capital Markets
Companies with Bitcoin treasuries often trade at premiums to their Bitcoin holdings, creating opportunities to raise capital through equity or debt offerings. Strategy, for example, regularly issues convertible bonds at low interest rates, using investor enthusiasm for Bitcoin exposure to secure favorable financing terms.
Understanding mNAV: The Premium Game
mNAV compares the market value of a company’s stock to the actual value of the Bitcoin they own. It shows how much extra investors are willing to pay for shares in the company, not just for the Bitcoin, but also for how the company manages it, talks about it, or builds around it.
Here’s how it works: If a company owns $100 million worth of Bitcoin, but its market value is $150 million, then mNAV equals 1.5, which means investors are paying 50% more than the actual Bitcoin value because they believe the company has strong management, future potential, or other valuable business assets.
And if the company’s mNAV is less than 1, then the stock is trading at a discount, i.e., investors are valuing the company less than the Bitcoin it owns (signaling low trust or bad performance).
So, once a company trades at a premium to its BTC holdings, it unlocks the ability to raise capital in powerful ways:
-
Issue more stock at high prices when trading at significant premiums.
-
Raise debt (like convertible bonds) backed by investor optimism at low interest rates.
-
Use the new funds to buy even more Bitcoin, driving up mNAV further.
-
Create a feedback loop where Bitcoin exposure inflates stock prices, enabling more capital raising.
5. Strategic Positioning and Investor Appeal
Adopting a Bitcoin treasury can position companies as forward-thinking and attract crypto-savvy investors. Many Bitcoin treasury companies have seen significant stock price appreciation, outperforming traditional businesses in their sectors.
Strategy: The Pioneer Bitcoin Treasury Company
When Michael Saylor pivoted Strategy (formerly MicroStrategy) into what he calls “a Bitcoin treasury company” in August 2020, he rewrote the playbook for corporate finance. Facing a struggling enterprise software business and cash eroded by inflation, Saylor made an unprecedented $250 million Bitcoin bet that transformed the company into one of Wall Street’s most watched stocks.
“We are a Bitcoin treasury company, so we are securitizing Bitcoin.”
— Michael Saylor, Chairman, Strategy
As of July 2025, Strategy holds over 628,000 BTC, making it the world’s largest corporate Bitcoin holder. More importantly, the company has perfected what critics call the “infinite money glitch” (a sophisticated capital market strategy that leverages Bitcoin’s appreciation to continuously raise more funds).
The Playbook That Changed Everything
Strategy’s approach goes far beyond buy-and-hold. The company consistently trades at a premium to its Bitcoin holdings (mNAV often exceeding 2-3x), meaning investors pay $200-300 for every $100 of Bitcoin it owns. This allows Strategy to issue convertible bonds at low interest rates and sell overvalued stock to buy undervalued Bitcoin, creating a powerful feedback loop.
This strategy has grown Strategy’s market cap from under $2 billion to over $80 billion at its peak, while accumulating Bitcoin at an average cost basis significantly below market prices.
Beyond Financial Engineering
Saylor has repositioned Strategy as a “Bitcoin development company” rather than a software firm that owns Bitcoin. The company actively advocates for Bitcoin adoption, develops Bitcoin-related solutions, and serves as a proxy for institutional investors seeking Bitcoin exposure without direct ownership.
Strategy’s radical transparency around its Bitcoin operations—detailed quarterly reports on holdings and acquisition strategies—has built trust with investors who view it as the most credible way to gain leveraged Bitcoin exposure in traditional markets.
The “Saylor playbook” has inspired over 180 companies to add Bitcoin to their treasuries, fundamentally changing how corporations think about treasury management in an era of monetary uncertainty.
Companies Holding Bitcoin: A Diverse Global Movement
Following Strategy’s playbook, more than 180 companies, including Metaplanet, Tesla, GameStop,, and Semler Scientific, among others, have BTC in their corporate treasuries today. In the last three quarters, public and private companies have bought more Bitcoin than BTC ETFs.
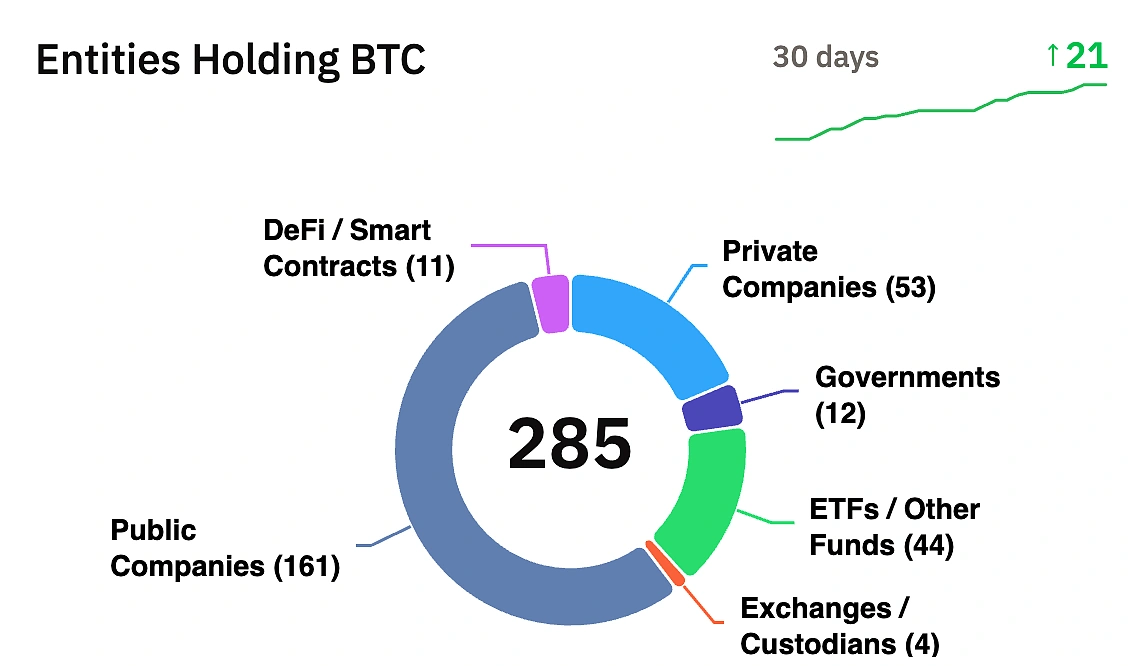
Bitcoin treasury adoption spans diverse industries, showing this isn’t just a tech phenomenon:
|
Company |
Ticker |
Core Business |
BTC Held |
BTC as % of Market Cap |
mNAV |
|
Strategy (MicroStrategy) |
MSTR |
Enterprise Software / Bitcoin Development |
607,770 |
62.8% |
1.59 |
|
Metaplanet Inc. |
3350.T |
Bitcoin Treasury Company (Japan) |
17,132 |
36.8% |
2.71 |
|
Tesla |
TSLA |
Electric Vehicles |
11,509 |
0.1% |
745.39 |
|
Semler Scientific |
SMLR |
Healthcare Technology |
5,021 |
111.0% |
0.90 |
|
GameStop |
GME |
Games and Entertainment |
4,710 |
5.4% |
18.65 |
|
Jasmine International PCL |
JAS.BK |
Telecommunications and Technology (Thailand) |
506.4 |
16.6% |
6.02 |
|
Alliance Resource |
ARLP |
Coal Production |
~510.9 |
1.7% |
59.21 |
This diversity demonstrates that Bitcoin treasuries aren’t limited to crypto-native companies—traditional businesses across sectors are adopting this strategy.
How Bitcoin Corporate Treasuries Work
Implementing a Bitcoin treasury involves several key steps and considerations:
1. Strategic Planning
Companies must determine appropriate allocation percentages, risk tolerance, and integration with existing treasury operations. Most start conservatively, allocating 5-10% of cash reserves to Bitcoin before potentially increasing exposure.
2. Acquisition Methods
-
Direct purchase with excess cash.
-
Debt financing through convertible bonds or loans.
-
Equity offerings to raise capital specifically for Bitcoin purchases.
3. Custody and Security
Secure storage is critical. Companies typically use:
-
Qualified custodians like Coinbase Custody, BitGo, or Fireblocks.
-
Multi-signature wallets that require multiple approvals for transactions.
-
Cold storage for long-term holdings.
-
Insurance coverage to protect against theft or loss.
4. Accounting and Compliance
The 2025 implementation of FASB’s ASU 2023-08 requires fair-value accounting for Bitcoin, allowing companies to report both unrealized gains and losses. This provides more accurate financial reporting compared to previous impairment-only accounting rules.
5. Risk Management
Companies implement policies for:
-
Volatility management and stress testing.
-
Liquidity planning for operational needs.
-
Regulatory compliance across jurisdictions.
-
Governance controls to prevent unauthorized transactions.
Risks and Challenges of Bitcoin Corporate Treasuries
Corporate Bitcoin treasuries are a growing trend, but many challenges still mar their efficacy.
Volatility and Financial Impact
Bitcoin’s price can fluctuate dramatically—sometimes 20-50% in months. This volatility directly impacts company balance sheets and can create earnings unpredictability that concerns traditional investors.
Regulatory Uncertainty
Cryptocurrency regulations are still evolving globally. Companies must navigate complex compliance requirements that vary by jurisdiction and may change significantly over time.
Security and Custody Risks
Unlike FDIC-insured bank deposits, Bitcoin requires sophisticated security measures. Companies face risks of:
-
Hacking or theft of digital assets.
-
Loss of private keys making Bitcoin permanently inaccessible.
-
Operational errors in transactions or storage.
-
Counterparty risk with custodial services.
Auditing and Transparency Challenges
Auditing Bitcoin holdings presents unique difficulties. Many companies don’t publicly disclose wallet addresses for security reasons, making independent verification challenging. For instance, Saylor, whose company’s books are audited by KPMG, one of the Big Four, states, “If you publish your wallets, that’s an attack vector for hackers, nation-state actors, every type of troll imaginable.”
The 2023 Public Company Accounting Oversight Board report highlighted insufficient audit evidence for digital assets. There’s no way to know if the Bitcoins displayed as assets in a company’s ledger have been pledged or lent elsewhere.
Capital Erosion Risk
If Bitcoin prices decline significantly, companies could face substantial losses. Most recent adopters purchased Bitcoin above $90,000; prolonged price declines could create liquidity issues or force asset sales at losses.
Mathew Sigel, head of digital assets at VanEck, says, “Once you are trading at net asset value, shareholder dilution is no longer strategic.” Semler Scientific saw a 45% fall in its stock prices, and its market cap dropped below its BTC reserves.
Why Major Tech Companies Are Saying ‘No’
Despite potential benefits, tech giants like Meta, Amazon, and Microsoft have overwhelmingly rejected Bitcoin treasury proposals:
In 2025, over 90% of Meta shareholders voted against a Bitcoin treasury proposal. Nearly 5 billion votes opposed the idea, with only 3.9 million in favor – less than 0.1% support.
Common Concerns from Big Tech
-
Volatility Concerns: Bitcoin’s price swings don’t align with stable treasury management principles.
-
Regulatory Uncertainty: Evolving crypto regulations create compliance risks.
-
Core Business Focus: Companies prefer focusing resources on primary operations rather than financial speculation.
-
Fiduciary Responsibility: Board members worry about breaching duties to shareholders by investing in speculative assets.
Conservative Treasury Philosophy
Large tech companies typically maintain conservative treasury strategies focused on:
-
Capital preservation over speculation.
-
Predictable liquidity for operational needs.
-
Risk minimization rather than return maximization.
-
Stakeholder stability expectations.
Future Outlook: The Evolution of Corporate Treasuries
Bitcoin corporate treasuries represent either a transformative shift in finance or a speculative bubble, depending on perspective. Several factors will determine their long-term viability:
Regulatory Clarity
Clearer regulations and accounting standards could encourage broader adoption by reducing compliance uncertainty. With Trump’s executive order of implementing a strategic Bitcoin reserve, government acceptance of Bitcoin may provide additional legitimacy.
Market Maturation
As Bitcoin markets mature and volatility potentially decreases, more conservative companies might consider treasury allocation. At the same time, institutional infrastructure will continue improving, offering better custody solutions and insurance products.
Economic Conditions
Continued inflation concerns and monetary uncertainty could drive more companies toward alternative stores of value.
Competitive Pressure
If Bitcoin treasury companies consistently outperform traditional competitors, market pressure might force broader adoption despite inherent risks.
Conclusion
The rise of BTC treasury companies could be a fad or the most significant transformation not many anticipated in the history of capital markets. Bitcoin is now the primary corporate asset rather than an alternative investment for many firms.
Public and private companies hold almost 6% of the total Bitcoin supply today, and many are rushing to buy the 450 bitcoins being mined every day until the next halving strikes.
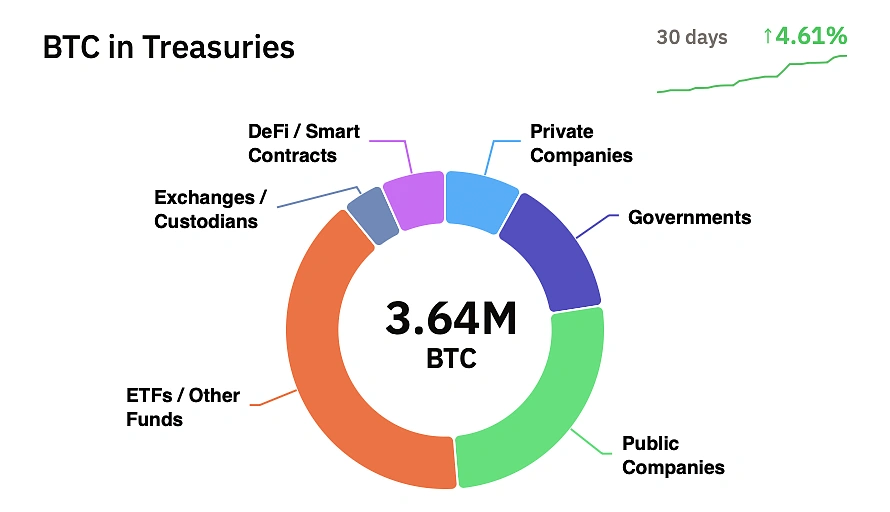
More firms are adding BTC to their treasuries to reduce counterparty risk and currency debasement and add diversification to their corporate holdings. However, the companies must assess the risk-to-reward ratio and adopt a balanced approach to BTC or any other crypto exposure.
Success stories like Strategy have demonstrated the potential upside, but recent rejections by major tech companies highlight ongoing skepticism about volatility and risk management.
For companies considering Bitcoin treasuries, careful planning, robust risk management, and clear strategic rationale are essential. This isn’t about riding crypto trends—it’s about making informed financial decisions in an era of monetary uncertainty.
Whether Bitcoin corporate treasuries become mainstream or remain niche depends largely on regulatory development, market maturation, and companies’ risk tolerance evolution. What’s certain is that they’ve already changed the conversation about corporate treasury management permanently.
Disclaimer: This article is only for informational purposes and should not be taken as investment or financial advice. Always do your own research before investing in any financial product or cryptocurrency.
